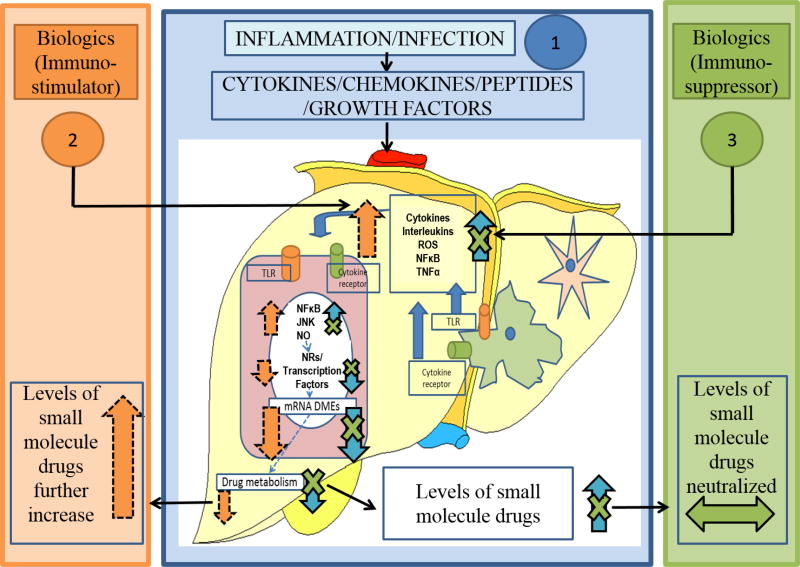
Figure 4.
Mechanism of Biologics-SMDs interaction. 1) In infection/inflammation disease states, plasma levels of cytokines/chemokines/peptides and growth factors are elevated. These factors act on the liver to activate kupffer cells to release pro-inflammatory cytokines. These intrinsic as well as the circulatory cytokines act on the hepatocytes through the cytokine receptors. Furthermore, the TLRs on the hepatocytes are activated, to induce cell-signaling pathways, leading to the down-regulation of basal transcription factors, NRs and DMEs. This leads to disruption of drug metabolism/clearance. 2) Upon treatment with biologics which are immunostimulators, cytokines in the liver are elevated further, thus potentiating the down-regulation of DMEs, causing more severe disruption of drug metabolism/clearance and increasing the levels of SMDs. 3) In contrast, biologics which are immunosuppressors, attenuate inflammatory disease-mediated elevation of cytokines and restore the expression/activity of DMEs and ultimately levels of SMDs are neutralized.