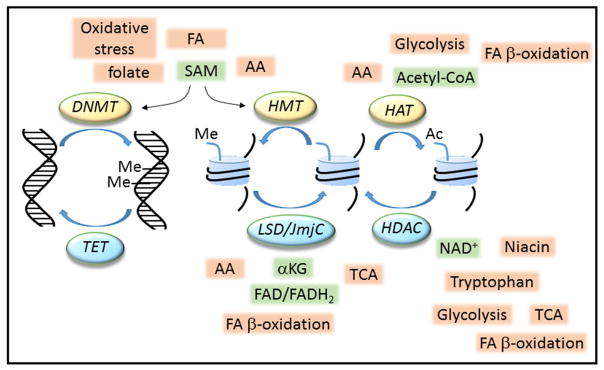
Figure 3. Nutrients regulate epigenetic modifications.
Carbohydrate, fatty acid (FA) and amino acid (AA) metabolism produces intermediates, including S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM), acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) and α-ketoglutarate (αKG), which act as co-substrates for epigenetic, chromatin modifying enzymes. DNA methyltrasferases (DNMT) methylate (Me) DNA, whereas histone methylation (Me) and acetylation (Ac) are mediated by methyltranseferases (HMT) and acetyltransferases (HAT), respectively. Histone demethylation and deacetylation are also subject to nutrient regulation via the action of demethylases (LSD/JmjC) and deacetylases (HDAC). Demethylation of DNA occurs passively or via enzymes of the Ten-eleven Translocation (TET) family. Together these modifications regulate heritable patterns of gene expression. TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle.