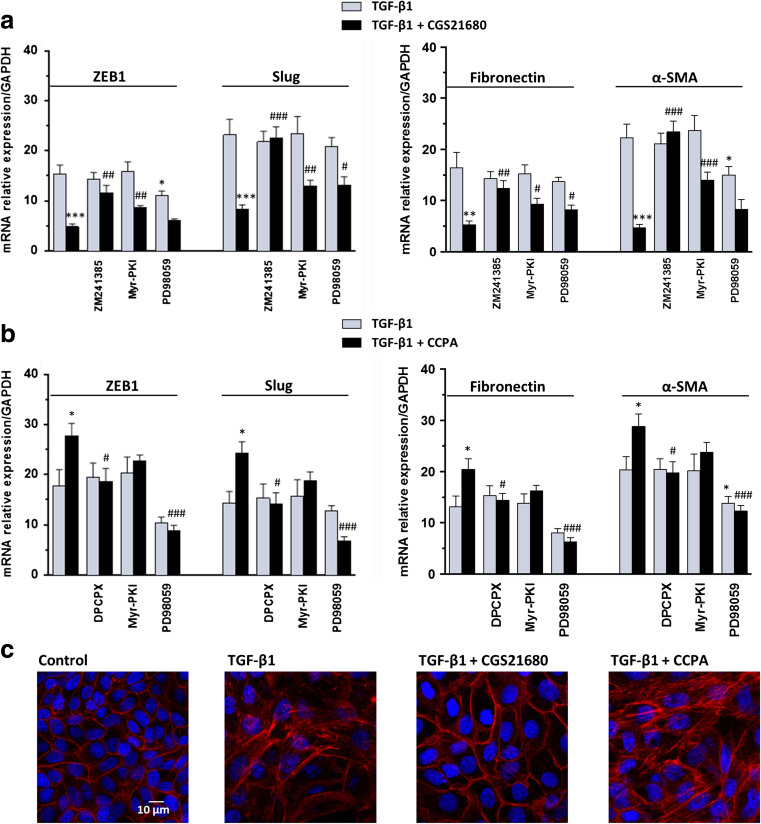
Fig. 4.
Effects of P1 adenosine receptor agonists on TGF-β1-induced EMT. a MDCK cells were challenged to 5 ng/mL TGF-β1 for 48 h in the absence or presence of the selective A2AR agonist, 50 nM CGS21680, or b the selective A1R agonist, 50 nM CCPA. The expression of ZEB1, Slug (left) and Fibronectin, α-SMA (right) was evaluated by RT-PCR analysis. A2AR or A1R antagonists, 50 nM ZM241385 or 100 nM DPCPX, as well as PKA or ERK 1/2 inhibitors, 5 μM Myr-PKI or 10 μM PD98059, were added to culture medium 30 min before TGF-β1 treatment or co-treatment with TGF-β1/A2A or A1R agonists until the end of the experiment. Each column represents the mean ± SEM of at least five independent experiments, and it is expressed as relative amount of mRNA normalized to GAPDH. Student’s t test: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. TGF-β1-treated cells; # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, ### P < 0.001 vs. TGF-β1/A2AR or A1R agonist-treated cells. c Representative photomicrographs of MDCK cells. Cells were challenged with 5 ng/mL TGF-β1 in the absence or presence of 50 nM CGS21680 or 50 nM CCPA for 48 h. The sub-confluent monolayers were stained with rhodamine-phalloidin (red) and nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars: 10 μm