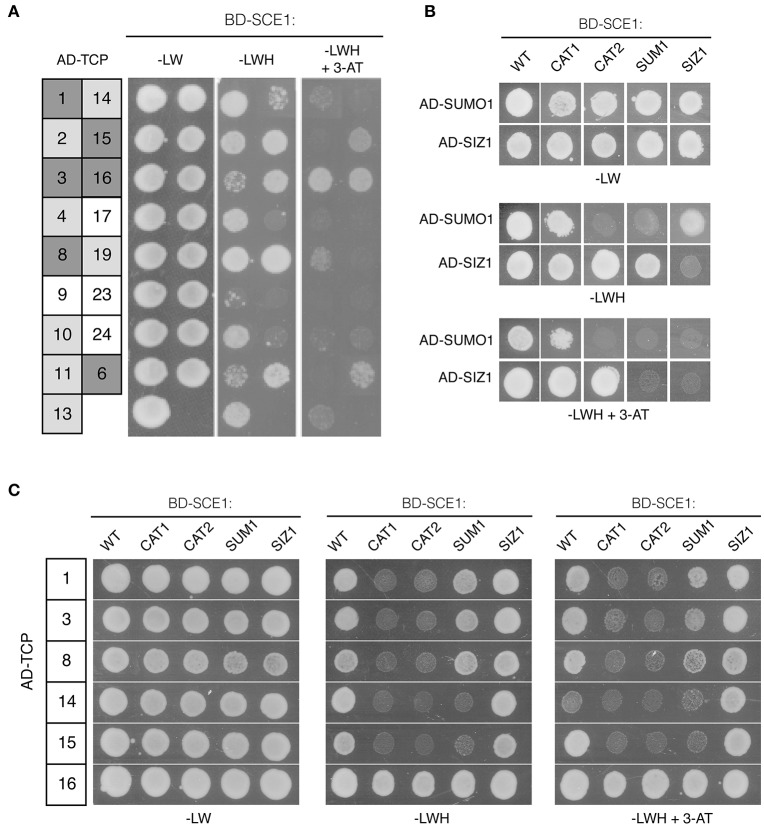
Figure 3.
An intact catalytic pocket of SCE1 is essential for its interaction with the different TCPs. (A) Y2H interaction assay between wild type SCE1 (BD-SCE1) and different Arabidopsis TCPs (AD-TCP; the number denotes the TCP TF). Gray boxes reflect a positive protein-protein interaction with dark gray depicting yeast growth on selective medium (–LWH) supplemented with 1 mM 3-AT (strong interaction), while light gray depicts yeast growth only on −LWH (weak interaction). (B) Y2H assay showing the interaction between different SCE1 variants and SUMO1 or SIZ1. SCE1 variants: CAT1, catalytically dead-variant of SCE1(C94S); CAT2, catalytically dead-variant of SCE1 in which the ΨKxE binding pocket is mutated (Y87A C94S C94S D129A); SUM1, SCE1 variant in which the non-covalent binding site of SUMO is mutated (R14E R18E H20D); SIZ1, SCE1 variant with mutations in the SIZ1 binding site (P70A P106A). None of these SCE1 variants showed auto-activation (Figure S1). (C) Six TCPs, which strongly interacted with SCE1 (A), were tested for their interaction with SCE1. Except for TCP16 all of the tested TCPs failed to interact with SCE1CAT1 and SCE1CAT2. Both TCP14 and TCP15 fail to interact with SCE1SUMO1. –LW, minimal medium lacking Leu/Trp; –LWH, medium lacking Leu/Trp/His (weak interaction); + 3-AT (1 mM), inhibitor for low-level constitutive expression of the HIS3 reporter gene. Yeast growth was scored after 3 days at 30°C and the experiment was performed three times with similar results.