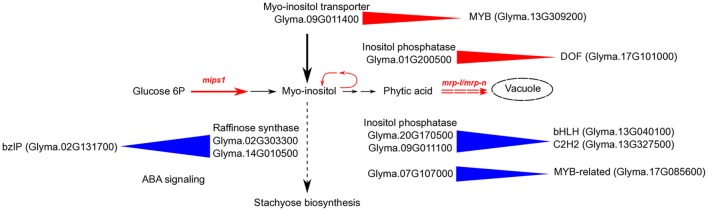
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of regulation of inositol pathway in low phytic acid soybean mutants. Black arrows represent the flow of myo-inositol in multiple pathways in non-mutant plants. Red solid arrows with mips1 label represent mutation in the rate-limiting first step of inositol pathway, catalyzed by myo-inositol phosphate synthase. Red dashed double arrows represent mutation in MRP-type ABC transporters (mrp-l/mrp-n) that block the last step in the inositol pathway, which is the movement of phytic acid to storage vacuoles. The myo-inositol pathway is blocked in single mutant (mips1 or 1mlpa) at the first step, and in triple mutant (mips1/mrp-l/mrp-n) at both first and last steps. Blue triangles represent predicted positive regulation in non-mutants. Red triangles represent predicted gene regulations in both single and triple mutants. For example, a bZIP transcription factor (Glyma.02G131700) is homologous to the well-known ABF1, and is involved in ABA signaling. This transcription factor is predicted to positively regulate raffinose synthase in non-mutant genotypes. A DOF transcription factor (Glyma.17G101000) is predicted to regulate inositol phosphatase in mutants. This enzyme is involved in breakdown of inositol pathway intermediates to form myo-inositol. A MYB transcription factor (Glyma.13G309200) is predicted to regulate myo-inositol transporter in mutants.