Fig. 1.
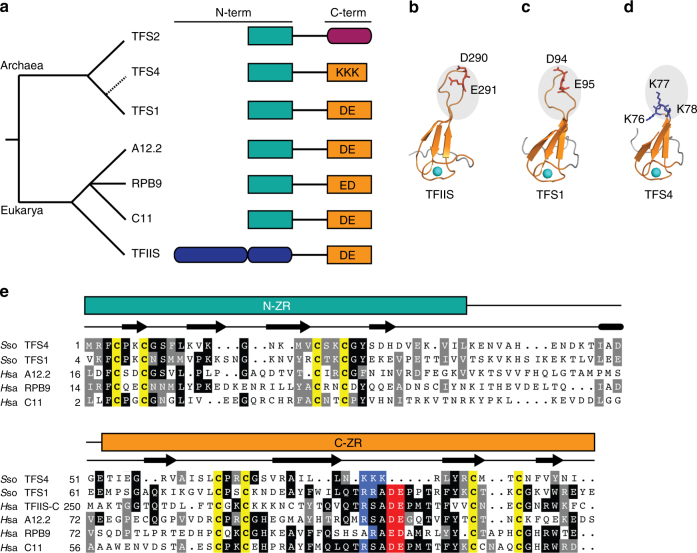
Evolutionary conservation of TFIIS-like proteins. a Phylogenetic distribution and domain conservation of TFS-related proteins in archaea and eukaryotes. Gene duplication events specific to the Sulfolobales order are shown as dashed lines. Zinc ribbon and α-helical domains as symbolized by rectangles and ellipses, respectively. b–d Structural homology between yeast TFIIS (b), Sso TFS1 (c) and Sso TFS4 C-ZR (d). Structural models of the C-ZR domains of TFS1 (C-score: 0.63; TM-score: 0.80±0.09) and TFS4 (C-score: −0.03; TM-score: 0.71±0.12) were prepared using PHYRE 256. The two carboxylate residues (TFIIS and TFS1) and the lysine residues (TFS4) are highlighted as stick representation in red and blue, respectively. Zn2+ ions are shown as cyan spheres. e Sequence alignment of of Sulfolobus solfataricus (Sso) TFS4 (AAK42105.1), Sso TFS1 (AAK40629.1), Homo sapiens (Hsa) RPB9 (P36954.1), Hsa A12.2 (Q9P1U0.1), Hsa C11 (AAD31424.1), Hsa TFIIS C-ZR (AAH72460.1). Secondary structure prediction of Sso TFS1 is shown above the alignments