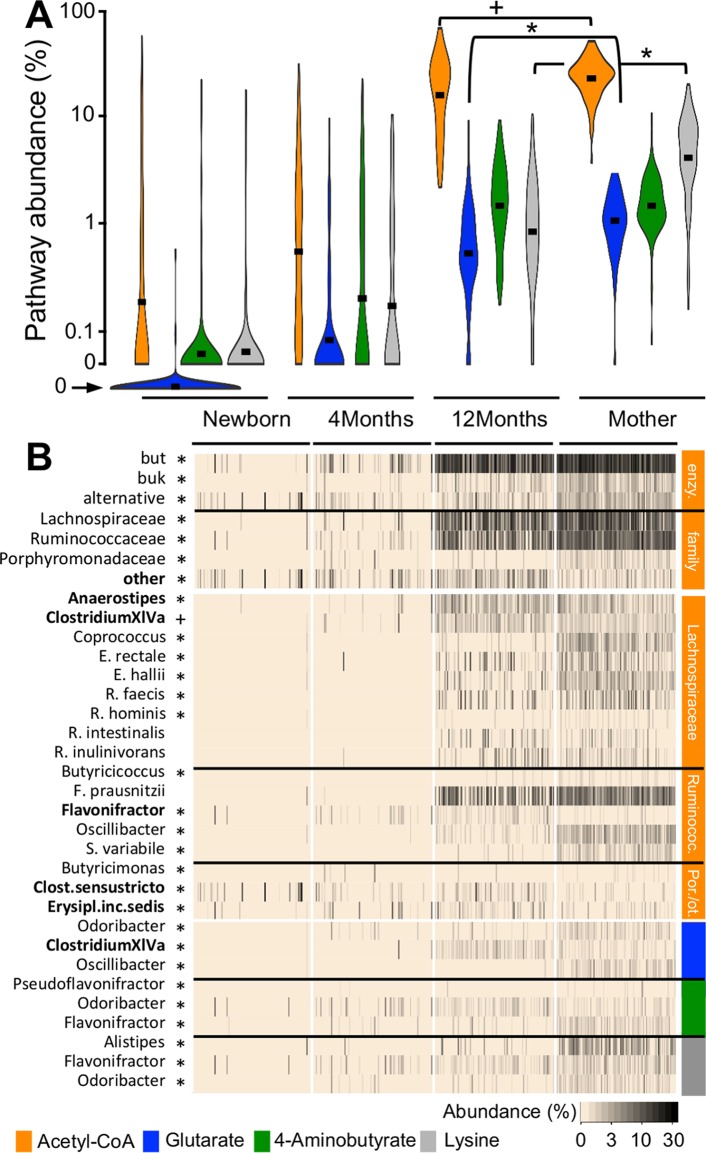
FIG 3 .
Succession of the butyrate-producing community after birth. Samples from mothers (n = 100) and their infants (1 week [n = 98], 4 months [n = 100], and 12 months [n = 100] after birth) were analyzed. (A) Abundances of bacteria exhibiting respective pathways as percentages of total bacteria (results for the glutarate pathway in newborns were manually shifted down to fit the plot layout). (B) Abundances of acetyl-CoA pathway groups, i.e., “enzyme” (cumulative abundance of all taxa exhibiting distinct terminal enzymes; enzy.) and “family” (cumulative abundance of all taxa of respective taxonomic families), as well as abundances of major individual taxa. Pathway affiliations of taxa are indicated by the color bars; members of the acetyl-CoA pathway are arranged on the family level. Significant differences (P < 0.05; *) and trends (P < 0.1; +) between mothers and their 12-month-old infants based on FDR-corrected pairwise Student t tests (pathway abundances) and Wilcoxon signed-rank tests (B) are illustrated; taxa enriched in 12-month-old infants are highlighted in bold. Black bars in violin plots represent mean values. Ruminococ., Ruminococcaceae; Por./ot., Porphyromonadaceae/other families.