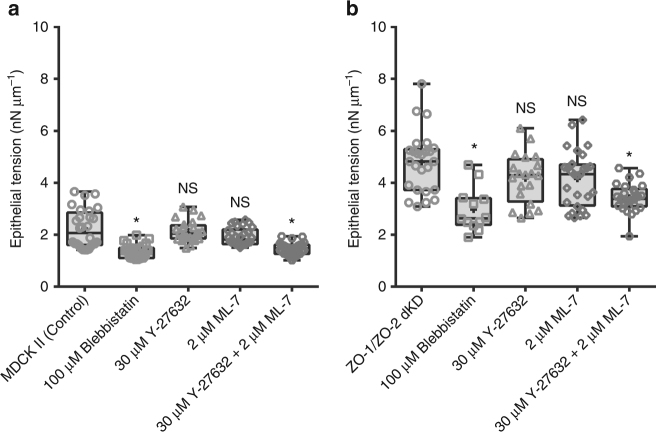
Fig. 4.
Apical surface tension in polarized epithelium is mostly determined by myosin II motor ATPase activity rather than ROCK signaling or MLCK activity. Confluent monolayers of MDCK II controls and ZO-1/ZO-2 dKD cells were treated with 100 µM blebbistatin, 30 µM Y-27632, 2 µM ML-7, or 30 µM Y-27632 + 2 µM ML-7 pharmacological drugs for 15 to 20 h. a Epithelial tension of MDCK II control untreated polarized monolayers, and treated either with 100 µM blebbistatin, 30 µM Y-27632, 2 µM ML-7, or 30 µM Y-27632 + 2 µM ML-7. b Epithelial tension of MDCK II ZO-1/ZO-2 dKD untreated polarized monolayers, or treated either with 100 µM blebbistatin, 30 µM Y-27632, 2 µM ML-7, or 30 µM Y-27632 + 2 µM ML-7. Myosin II activity inhibition significantly reduces the epithelial tension, whereas individual inhibition of ROCK signaling or MLCK activity do not cause a significant change on epithelial tension. Interestingly, combined inhibition of ROCK signaling and MLCK activity significantly reduces the epithelial tension. Data are represented as mean ± s.d.; * indicates significant difference in comparison with control P < 0.05 (unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test with Welch’s correction); NS nonsignificant differences in comparison with control P > 0.05(unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test with Welch’s correction); number of measurements pooled for 2–3 independent experiments for each condition, n = 28, 27, 24, 30, and 29 for control, 100 µM blebbistatin, 30 µM Y-27632, 2 µM ML-7, and 30 µM Y-27632 + 2 µM ML-7, respectively, and n = 25, 15, 20, 28, and 28 for ZO-1/ZO-2 dKD, 100 µM blebbistatin, 30 µM Y-27632, 2 µM ML-7, and 30 µM Y-27632 + 2 µM ML-7, respectively