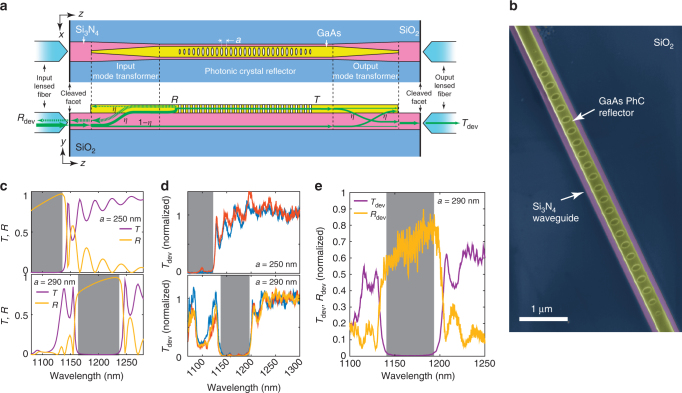
Fig. 4.
Characterizing mode transformer efficiency with a photonic crystal reflector. a Schematic of a PhC reflector device. Top: top-view. Bottom: cross-section. Green arrows indicate pathways taken by the optical signal injected at the input port. R and T stand for PhC modal power transmission and reflection spectra, and T dev, R dev transmission and reflection spectra through the entire device, including lensed fibers. b False-color SEM of fabricated GaAs PhC reflector (yellow) on top of a Si3N4 (pink) waveguide, on top of exposed SiO2 (blue). c FDTD-simulated TE modal transmission (T, purple) and reflection (R, yellow) spectra as a function of wavelength for the PhC (without mode transformers), for two different lattice constants a. d Experimental transmission spectra for various PhC reflectors with a = 250 nm (top) and a = 290 nm (bottom), normalized first to the transmission spectrum of a baseline Si3N4 waveguide (without GaAs sections), then to the mean transmission at wavelengths between 1250 and 1300 nm. Different colors indicate different devices. e Experimental transmission and reflection spectra for a PhC reflector with a = 290 nm, normalized to the transmission spectrum of a baseline Si3N4 waveguide. Gray areas have transmission <−15 dB in (c, d), <−20 dB in (e)