Fig. 4.
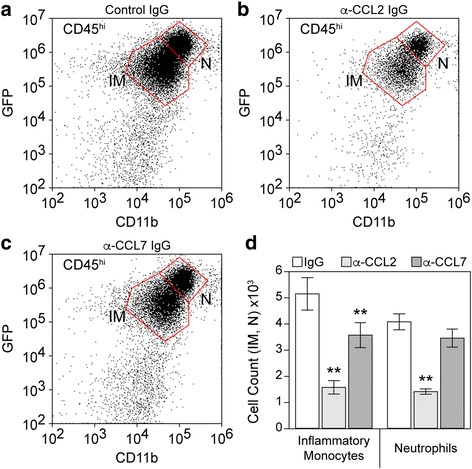
Inflammatory monocyte infiltration during acute infection is driven predominantly by CCL2. LysM:GFP mice received 20 μg goat IgG (a), 20 μg goat anti-CCL2 IgG (b), or 20 μg goat anti-CCL7 IgG (c) by intraperitoneal injection at − 12, 0, and + 12 h relative to time of infection. Brain-infiltrating leukocytes were collected at 24 hpi. The flow plots in (a–c) show cells in a CD45hi parent gate. The number of inflammatory monocytes (IM: CD45hiCD11b+GFPmid) and neutrophils (N: CD45hiCD11b++GFPhi) were counted; values are shown as mean ± 95% CI calculated from six mice per treatment condition in two separate experiments (3 × 2) (d). Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s method for pairwise comparison to control. Inflammatory monocytes were significantly reduced in both anti-chemokine groups compared to control IgG; neutrophils were significantly reduced only in the anti-CCL2 IgG group; **P < 0.001
