Fig. 1.
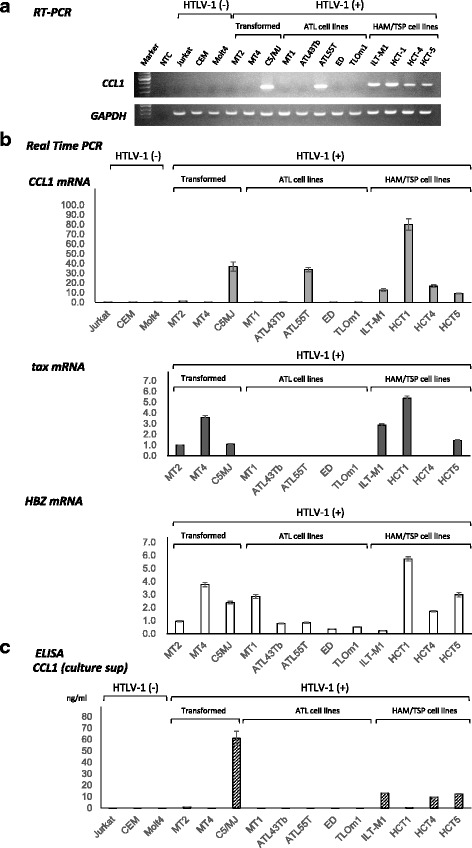
Preferential expression of CCL1 in Human T-cell leukemia virus type-1 (HTLV-1)-infected T-cell lines derived from patients with HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP). a. Expression of CCL1 was examined by RT-PCR in HTLV-1-infected and -uninfected T-cell lines. CCL1 mRNA was preferentially expressed in HTLV-1-infected human T-cell lines derived from patients with HAM/TSP (4 out of 4 tested), compared with HTLV-1-transformed T-cell lines (1 out of 3) and adult T-cell leukemia (ATL) cell lines (1 out of 4). b. The expressions of CCL1, tax, and HBZ were examined by real time PCR in HTLV-1-infected and -uninfected T-cell lines. CCL1 mRNA was preferentially expressed in HTLV-1-infected human T-cell lines derived from patients with HAM/TSP. The expression levels of the viral RNAs tax and HBZ were relatively high in T-cell lines derived from patients with HAM/TSP and HTLV-1-transformed T-cell lines when compared with those in ATL cell lines. c. CCL1 levels in culture supernatants from HTLV-1-infected and -uninfected human T-cell lines were assessed by ELISA. Supernatants were harvested when cells reached subconfluency. Significant levels of CCL1 was observed in the culture supernatants from HTLV-1-infected human T-cell lines derived from patients with HAM/TSP, whereas it was not detectable in any of the other cell lines tested except for the HTLV-1-transformed C5MJ cell line
