Figure 2.
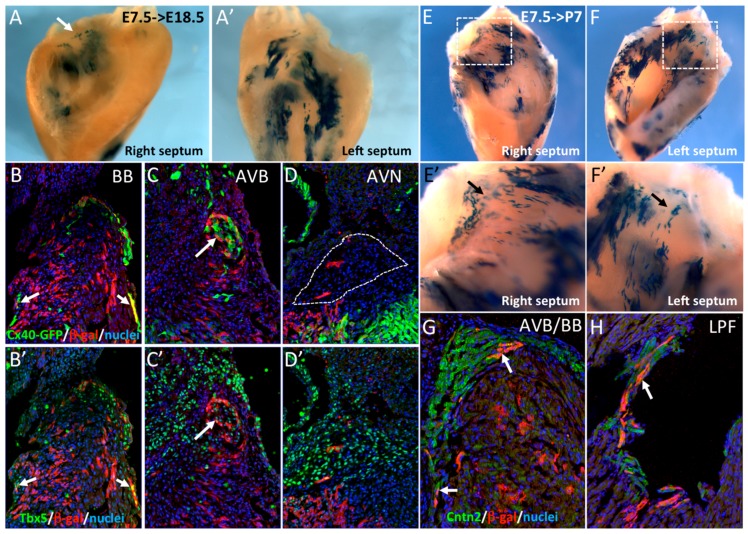
Early SMA+ cardiomyocytes contribute to the central ventricular conduction system. (A,A’) Whole-mount X-gal staining of the right and left sides of an E18.5 dissected septum after Cre induction at E7.5. Labeled cells are more abundant on the left side and sparse labeling is observed at the crest of the septum (arrow). (B–D) Immunofluorescence on sections of E18.5 hearts from Cx40GFP/+::SmaCre/+::R26RlacZ/+ mice after Cre activation at E7.5. SMA-derived cells are detected in the right and left bundle branches (BB) and are positive for Cx40-GFP (B) and Tbx5 (B’) (arrows). SMA+ cells participate to the AVB, that is also positive for Cx40-GFP (C) and Tbx5 (C’), but rarely to the AVN which is negative for Cx40-GFP (D) but positive for Tbx5 (D’). (E,F) Whole-mount X-gal staining of the right and left side of a P7 dissected septum after Cre induction at E7.5. High magnification of the septum crest (E’,F’) shows scattered X-gal positive cells in the region of the forming central VCS. (G,H) Immunofluorescence on sections of a P7 SmaCre/+::R26RlacZ/+ heart after Cre activation at E7.5 showing co-localization of SMA-derived cells and Contactin-2 (Cntn2) in the AVB (G) and left Purkinje fibers (H), indicated by arrows.