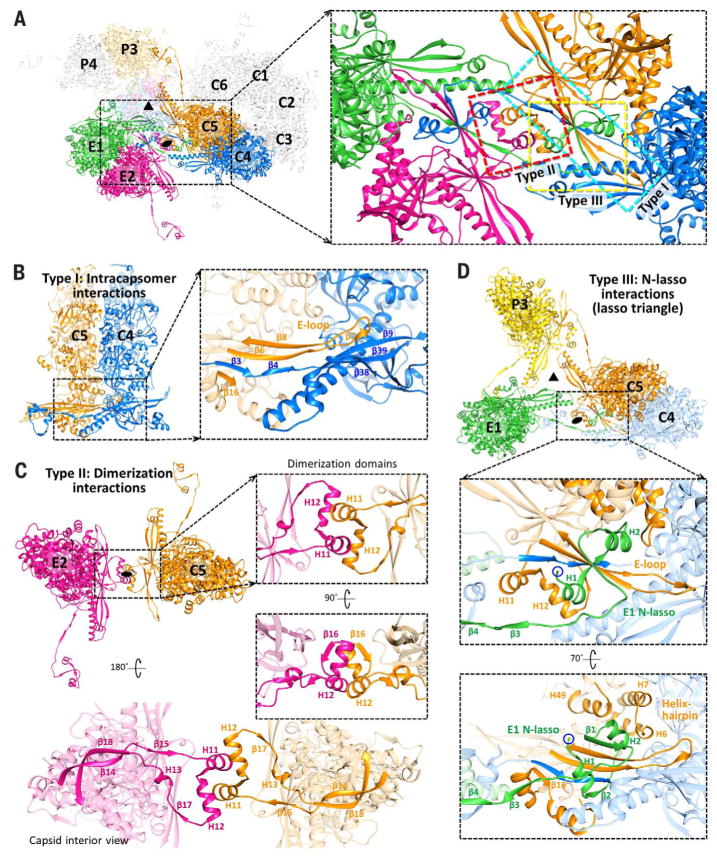
Fig. 4. Three classes of capsid floor–defining interactions.
(A) Overview of MCPs from C, E, and P hexons. Local threefold (triangle) and twofold (oval) axes are indicated. The inset shows the three major types of MCP-MCP interactions (boxed), subsequently illustrated in detail. (B) Intracapsomer interactions (type I) occur between adjacent MCPs within a capsomer and consist of two sets of floor region β-sheet augmentations (inset). (C) Dimerization interactions (type II) are intercapsomer interactions that occur between MCP dimerization domains across a local twofold axis. Insets show quasi-equivalent helix interactions between two dimerization domains. (D) N-lasso (type III) interactions are facilitated by an MCP N-lasso (green) that extends and lashes around the E-loop (orange) and N-lasso neck (blue) of two MCPs located diagonally across a local twofold axis (upper inset). Three pairs of N-lasso interactions form an enclosed lasso triangle around the local threefold axis. E1’s N-lasso also augments the existing β-sheet from C5 and C4’s type I interaction to form a seven-stranded β-sheet complex (lower inset). Helices from C5’s helix-hairpin (H6 and H7) and buttress (H49) domains form a helix bundle with E1 N-lasso’s H2, further securing E1’s N-lasso.