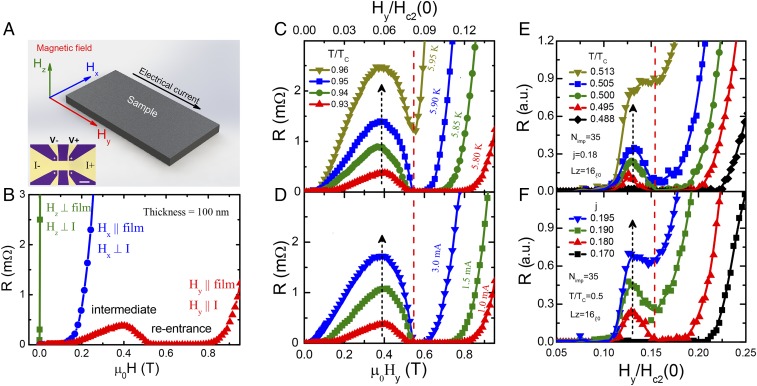
Fig. 1.
Temperature- and current-dependent parallel magnetic-field–induced reentrant superconductivity. (A) Schematics of the superconducting MoGe film in a triple-axis vector magnet. The out-of-plane magnetic field is perpendicular to both the film plane and the current direction. The in-plane magnetic field is parallel to the film plane and perpendicular to the current direction. The in-plane magnetic field is parallel to both the film plane and the current direction. The electrical current is applied parallel to the direction. A, Bottom Left Inset shows a photo of the micropatterned MoGe strip. (Scale bar, 50 μm.) (B) Magneto-resistance measured at K for a -nm-thick sample under magnetic fields in three orthogonal directions x (blue), y (red), and z (green), respectively. The resistance curve for the parallel field () shows a resistant state at intermediate fields and a reentrance of the superconducting state at higher fields. (C–F) Experimental results (C and D) and TDGL simulations (E and F) for the parallel field-dependent resistance at various temperatures (C and E) and at different currents (D and F). The zero-field superconducting critical temperature and zero-temperature upper critical field are K and T, respectively. Other simulation parameters, impurity density and sample thickness, are and (nm is zero-temperature coherence length).