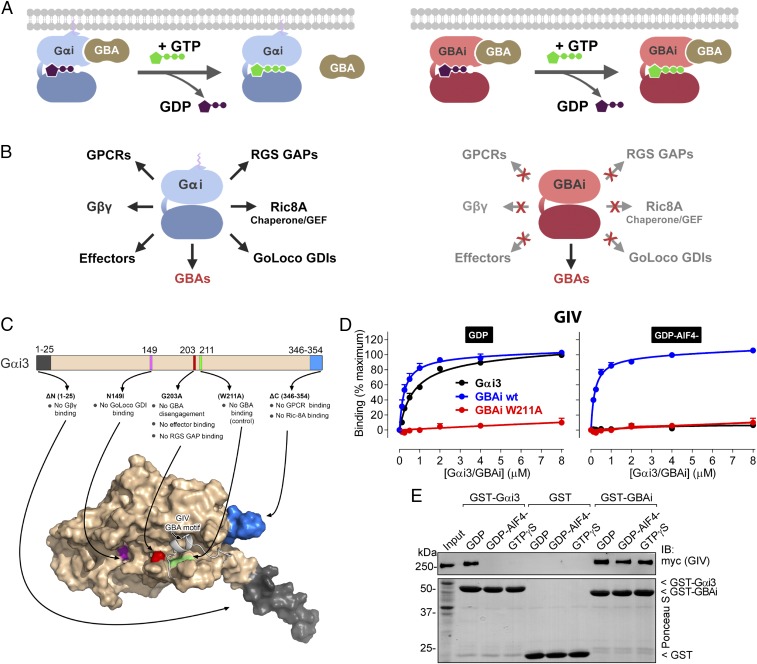
Fig. 1.
Rational design of GBAi, a specific inhibitor of GBA motifs. (A, Left) GBA motifs bind to Gαi in its inactive conformation (bound to GDP, purple), but not in its active conformation (bound to GTP, green). (A, Right) Desired property of Gαi-derived GBAi is that its binding to GBA motifs is not reversed upon nucleotide exchange of GDP for GTP, thereby resulting in constitutive high-affinity binding to GBA motifs in cells. (B) Desired property of Gαi-derived GBAi is a lack of binding to any other Gαi binding partner (GPCRs, Gβγ, effectors, RGS GAPs, GoLoco GDIs, or the chaperone/GEF Ric-8A; Left), thereby resulting in specific binding and inhibition of only GBA motifs (Right). (C, Top) Schematic of the modifications engineered into Gαi3 to generate GBAi. The G203A mutation disrupts a conformational change of the SwII region that normally occurs upon GTP binding and is required to bind effectors and RGS GAPs and, at the same time, precludes GBA binding. Additional mutations/deletions were introduced to prevent binding of Gβγ (ΔN 1–25), GPCRs (ΔC 346–354), GoLoco GDIs (N149I), and Ric-8A (ΔC 346–354). The W211A mutation is known to inhibit binding of Gαi3 to all GBA motifs described to date (i.e., from GIV, DAPLE, Calnuc, NUCB2) and is used as a negative control throughout this study. (C, Bottom) Localization of each modification is shown in a previously described model of Gαi3 bound to the GBA motif of GIV (33). (D) GBAi binds to the GBA motif of GIV with the same affinity as Gαi3, and GBAi-GIV binding is not affected by the activation mimetic GDP-AlF4−. Binding of a fluorescently labeled GIV peptide corresponding to its GBA motif (residues 1,671–1,701) to the indicated concentrations of purified His-tagged Gαi3 (black), GBAi wt (blue), or GBAi W211A (red) was determined by FP in the presence of GDP (Left) or GDP-AlF4− (Right). Data were normalized to maximal binding and fitted to a one-site binding model (solid lines). Results from three independent experiments are expressed as mean ± SEM. (E) GBAi binds the same to full-length GIV in the presence of GDP, GDP-AlF4−, or GTPγS, whereas Gαi3 binds GIV only in the presence of GDP. Lysates of HEK293T cells expressing full-length, myc-tagged GIV were incubated with GST, GST-Gαi3, or GST-GBAi immobilized on glutathione-agarose beads in the presence of GDP, GDP-AlF4−, or GTPγS (as indicated). Resin-bound proteins were eluted, separated by SDS/PAGE, and analyzed by Ponceau S-staining and immunoblotting (IB) as indicated. Input = 10% of the amount of lysate used in each pulldown. One experiment of two with very similar results is shown.