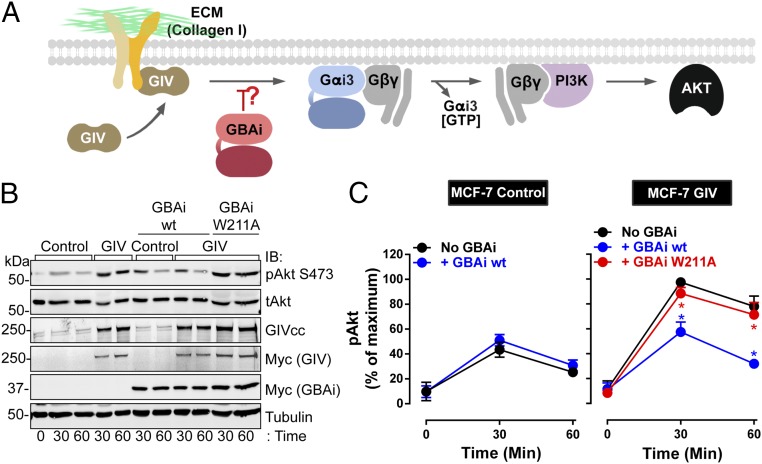
Fig. 4.
GBAi inhibits GIV-mediated potentiation of PI3K-Akt signaling upon integrin stimulation. (A) Schematic of a previously described mechanism (18) by which GIV potentiates PI3K-Akt signaling in response to integrin stimulation via its GBA motif. Stimulation of cells with extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins (e.g., collagen I) triggers the recruitment of GIV to the intracellular tail of integrins, which, in turn, leads to GBA-dependent G protein signaling. PI3K-Akt activation is achieved via free Gβγ subunits released from Gi heterotrimers upon GIV GBA action. (B and C) GBAi wt, but not GBAi W211A, inhibits GIV-mediated potentiation of Akt activation upon collagen I stimulation of MCF-7 cells. MCF-7 cells stably expressing a vector control or full-length GIV and transfected with myc-GBAi wt (blue) or myc-GBAi W211A (red), as indicated, were lifted from culture dishes; kept in suspension for 1 h in serum-free media (time 0); and stimulated by plating on collagen I-coated culture dishes for 30 and 60 min. One representative immunoblot result from four independent experiments is shown in A, and the results for the quantification of Akt activation [as determined by levels of phosphorylated Akt (pAkt)] expressed as mean ± SEM are shown in C. *P < 0.05, using the Student’s t test (blue, compared with no GBAi; red, compared with GBAi wt). tAkt, total Akt.