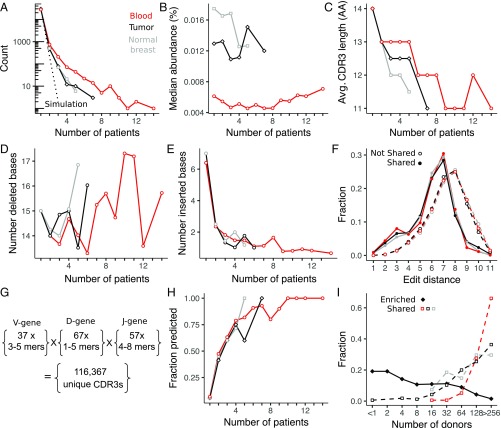
Fig. 6.
Interpatient T cell sharing of clonotypes between tissues. (A) Fraction of blood, tumor, and normal breast tissue sequences found in one (not shared) or more (shared) patients compared with the expected fraction by random sampling (dashed lines). (B) Median abundance of clonotypes detected in multiple patients is not sensitive to the degree of sharing. Compared with clonotypes that are not shared across multiple patients, shared clonotypes have a shorter CDR3 amino acid (AA) length (C), which can be attributed to a similar number of deleted (D) but fewer inserted (E), nucleotide bases in the junctional regions between V-D and D-J genes. Avg., Average. (F) Diversity of CDR3 sequences is estimated from the distribution of edit distances (length = 13 aa), which is shifted to lower values for shared sequences. Number and length of germline V-, D-, and J-gene amino acid sequence fragments used in a recombination model of low-diversity CDR3 sequences (G) and the fraction of CDR3 sequences detected by the model (H) are shown (details are provided in Materials and Methods). (I) Results from a database query of 585 healthy donors (18) indicate that shared CDR3 sequences are also likely to be shared in a population of healthy donors, whereas enriched CDR3 sequences are much less likely to be shared in the general population.