Figure 4.
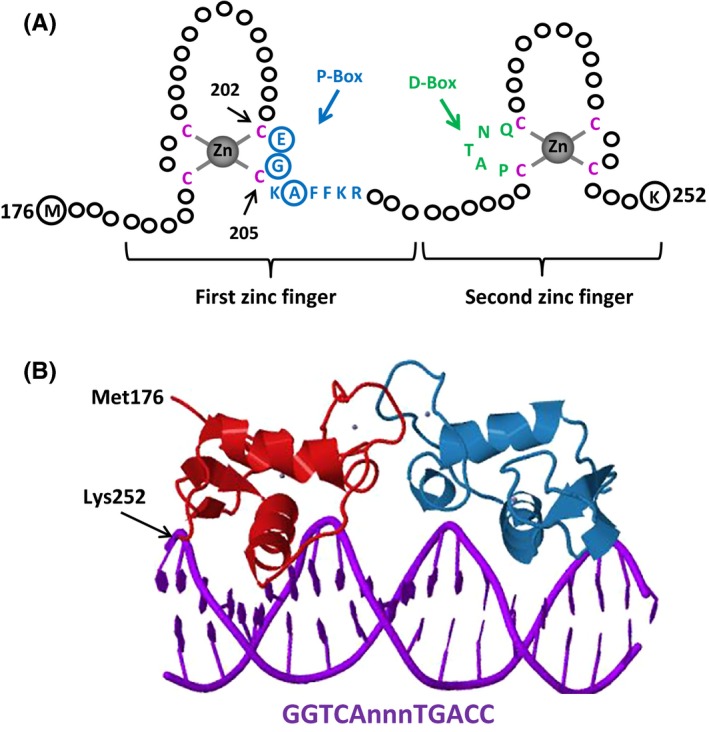
A, The DNA‐binding domain (DBD) of estrogen receptors (ERs). Schematized is the ERα–DBD. The DBD of ERα contains two zinc (Zn)‐binding motifs that are formed by a Zn ion (grey) that is coordinated by four cysteine residues (red). A region of the first Zn‐finger module, the P‐box, which contains amino acids (blue), particularly glutamic acid (E), glycine (G), and alanine (A) at positions 203, 204, and 207, respectively (circularized blue), determine the DNA‐binding specificity that is critical for sequence discrimination and binding to the estrogen response element. The residues (green) in the second Zn‐finger module, the D‐box, are involved in the discrimination of half‐site spacing. B, The tertiary structure of ERα–DBD (residues Met176–Lys252) as dimer‐bound to the consensus DNA sequence, GGTCAnnnTGACC (estrogen response element), with three non‐specific (n) intervening bases (Protein Data Bank identification: 1HCQ; Schwabe, et al61)
