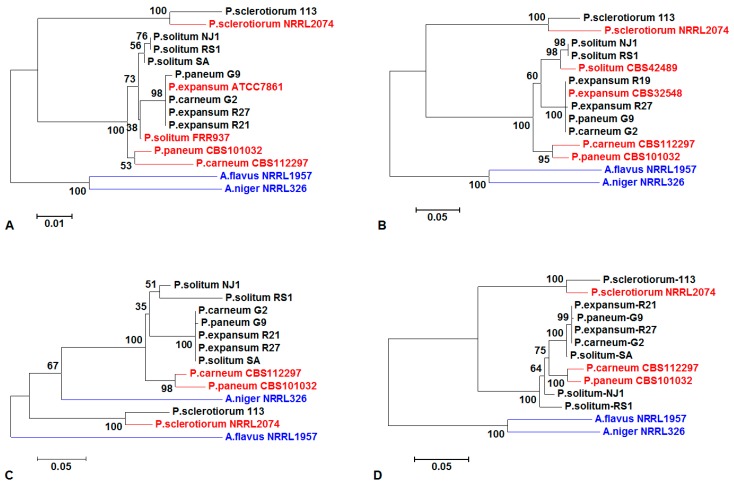
Figure 1.
Penicillium spp. phylogenetic trees constructed using markers (A) ITS; (B) benA; (C) CaM; and (D) combinations of the two or three genes. Nine of our isolates and nine ex-types from NCBI GenBank were phylogenetically arranged using available marker sequences. The nine strains obtained from NCBI were P. expansum ATCC7861 = P. expansum CBS32548, P. carneum CBS112297, P. paneum CBS101032, P. sclerotiorum NRRL2074, P. solitum CBS42489 = P. solitum FRR937, A. flavus NRRL1957, and A. niger NRRL326. All the Penicillium species from GenBank are shown in red; the two Aspergillus species are shown in blue; our own sequenced Penicillium species are shown in black. Three genes were used to perform sequences analysis in Figure 1D, except only two genes (ITS and CaM) were used in P. expansum R21 and P. solitum SA analysis.