Figure 6.
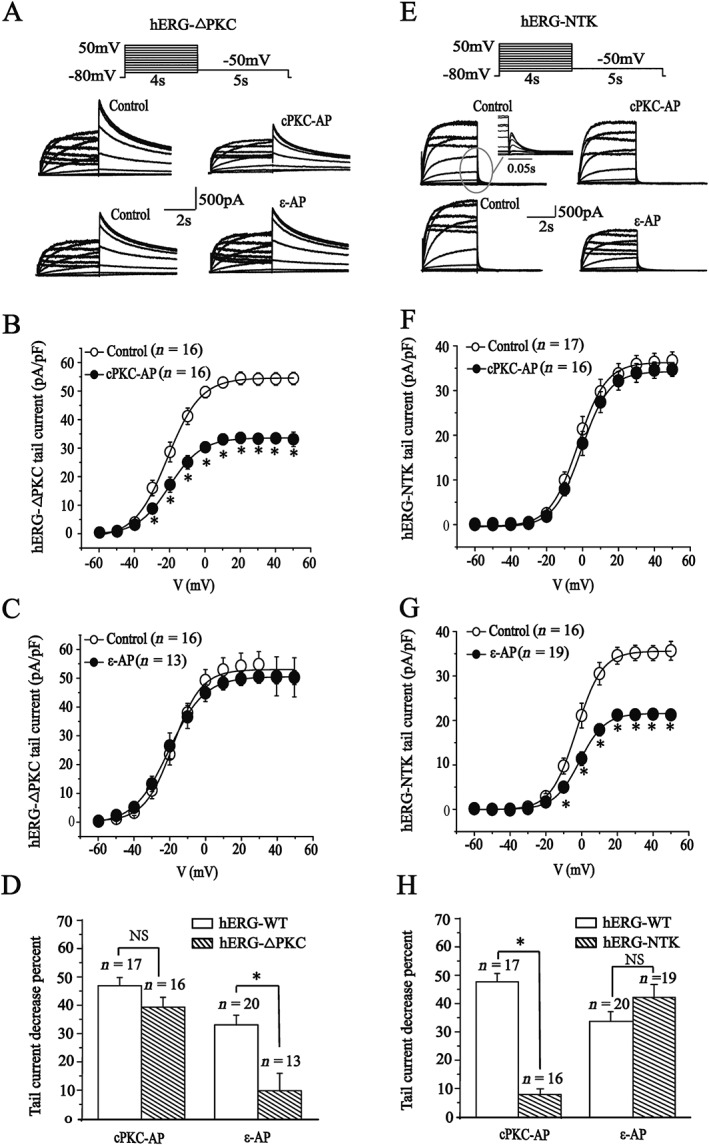
Effects of cPKC and PKCε activator peptides on mutant hERG‐ΔPKC and hERG‐NTK currents. (A, E) Representative current traces evoked using the voltage protocol shown in the presence of the scrambled peptides (control) or cPKC (cPKC‐AP) and PKCε activator peptides (ε‐AP). The inset shows an amplification of the tail currents. (B, F) I–V relationships for tail currents in the control and the presence of cPKC activator peptide (200 nM). (C, G) I–V relationships for tail currents in the control and the presence of PKCε activator peptide (200 nM). (D, H) Percentage decrease of tail currents measured at 0 mV depolarizing prepulse on the hERG‐WT and mutant currents. *P < 0.05, significantly different from control.
