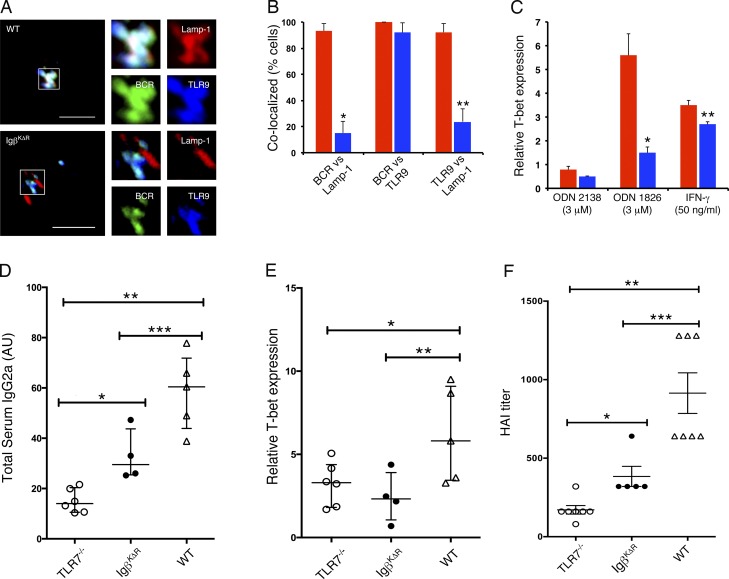
Figure 4.
Diminished BCR-dependent activation of endosomal TLRs. (A and B) WT and IgβKΔR splenocytes were stimulated with FITC-conjugated IgG- and IgM (H+L)-specific F(ab)2 antibodies for 30 min in vitro and then fixed, stained with antibodies specific for Lamp-1 and TLR9, and visualized by confocal microscopy. Representative images. Bars, 5 µm (A). Corresponding quantitation of WT (red) or IgβKΔR (blue) samples (n = 3); *, P = 1.3 × 10−15; **, P = 4.4 × 10−8 (B). (C) In vitro assay of T-bet induction in response to ODN 1826 or control ODN (2138) targeted through the BCR (n = 3); *, P = 0.004; **, P = 0.0003. (D and E) The indicated mouse strains were immunized with heat-inactivated influenza virus, boosted at day 21, and serum and splenic B cells were assayed at day 42. (D) IgG2a influenza-specific titers; *, P = 0.0054; ** P < 0.0001; ***, P = 0.0238. (E) Corresponding expression of T-bet mRNA in splenic B cells; *, P = 0.0484; **, P = 0.00507. (F) Serum hemagglutinin inhibition assay in response to influenza infection, day 27; *, P = ns; **, P < 0.0001; ***, P = 0.0034. For D–F, each symbol represents one mouse. Significance was determined by ANOVA in combination with Bonferroni multiple comparison test. P-values as indicated or **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001. Error bars represent mean ± SD.