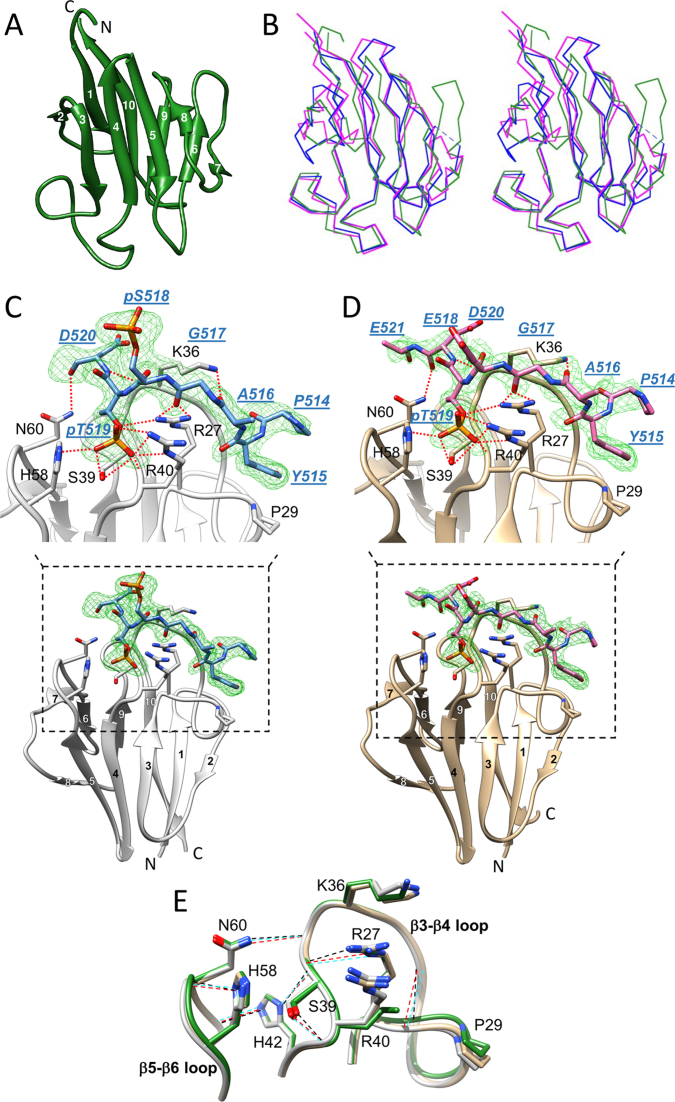
Figure 1.
Crystal structures of the APLF FHA domain unliganded and bound to a phosphorylated XRCC1 peptide. (A) Cartoon representation of apo-APLF FHA domain (green) with the 10 β-strands numbered. (B) Stereo view showing an overlay of α-carbon traces of APLF FHA (green) with the FHA domains of PNKP (blue) and APTX (magenta). The APLF FHA structures in complex with (C) XRCC1pSpT-9 diphosphopeptide (protein, light gray; peptide, blue) and (D) XRCC1EpT-9 monophosphopeptide (tan, protein; pink, peptide) are represented. Simulated annealing Fo-Fc omit maps of each phosphopeptide (green mesh) contoured at 3.0 σ for the diphosphopeptide and 2.5 σ for the monophosphopeptide are displayed. The peptide residues are annotated in blue with underlined, italic residue names, and the APLF FHA residues important for binding are annotated in black. Hydrogen-bond interactions are also depicted (red dotted line). (E) The topologies of the β3-β4 and β5-β6 loops in the APLF FHA domain for the apo (green), the XRCC1pSpT-9 diphosphopeptide-complexed (light gray), or the XRCC1EpT-9 -monophosphopeptide-complexed (tan) structures are represented. Hydrogen-bonds that sustain a binding-ready conformation are indicated by black, red or cyan dashed lines, respectively.