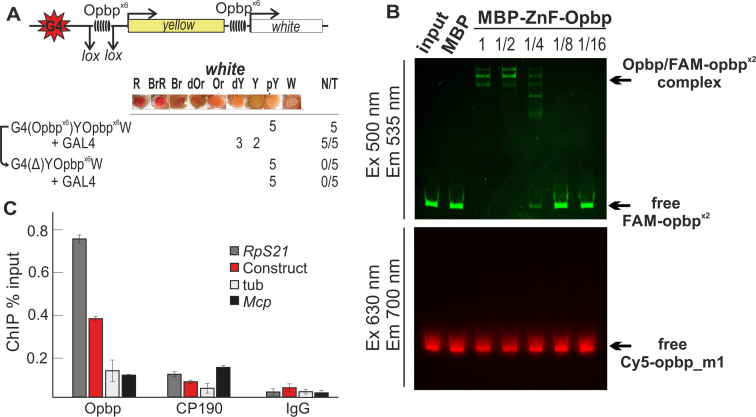
Figure 5.
Opbp sites are sufficient to mediate long-distance chromatin interactions. (A) Schematic of GAL4/white transgenic model system used to examine functional interactions between two Opbp binding sites (upper). GAL4 binding sites (indicated as G4) are at a distance of 5 kb from the white promoter. The level of white eye colour was assessed in five independent transgenic lines for each construct, the content of which is indicated as G4(Opbpx6)Y Opbpx6 W, etc ‘+GAL4’ indicates that eye phenotypes were examined after the induction of GAL4 expression (lower). The symbol Δ indicates the deletion of corresponding element from transgenic line. In the N/T ratio, N = number of transgenic lines that acquired a new white phenotype after GAL4 induction or deletion of a DNA fragment flanked by loxP sites, T = total number of transgenic lines examined. Level of eye pigmentation was estimated on an arbitrary nine-grade scale, from wild-type expression (R—red), BrR—brown-red, Br—brown, dOR—dark orange, Or—orange, dY—dark yellow, Y—yellow, pY—pale yellow, W—white. (B) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay of recombinant Zinc finger domains of Opbp with a DNA fragment containing Opbp binding sites used in the transgenic construct. Zinc finger domains of Opbp fused with MBP (7.2 ng) or alone MBP (5.2 ng) was incubated with fluorescently labeled DNA fragments; Opbp binding sites labeled with FAM (wt) and a fragment with mutated Opbp site labeled with Cy5 (used as a negative control). Signals were detected for FAM-labeled fragment at the Ex 500 nm/Em 535 nm and for Cy5-labeled fragment at the Ex 630 nm/Em 700 nm. Specificity of interaction was demonstrated by incubation of DNA fragments with different amount of Opbp protein presented as a series of 2-fold dilutions. The specific Opbp bound region (indicated by arrow) decreased with decreasing Opbp protein, as seen by the decrease in FAM-signal. Note, no binding was observed on the mutated Opbp site (Cy5 signal). (C) Opbp binding sites are sufficient to recruit both Opbp and CP190 to a transgenic loci. Chromatin was isolated from embryos carrying the construct and treated with antibodies to Opbp and CP190. Nonspecific IgG was used as a negative control. ChIP recovery is presented as a percentage of input DNA. The tubulin-γ37C (tub) coding region (devoid of binding sites for the test proteins) was used as a negative control; Mcp and Rps21 as CP190-binding regions, Rps21 as Opbp-binding region were used as positive controls. Error bars indicate standard deviations of quadruplicate PCR measurements for three independent experiments.