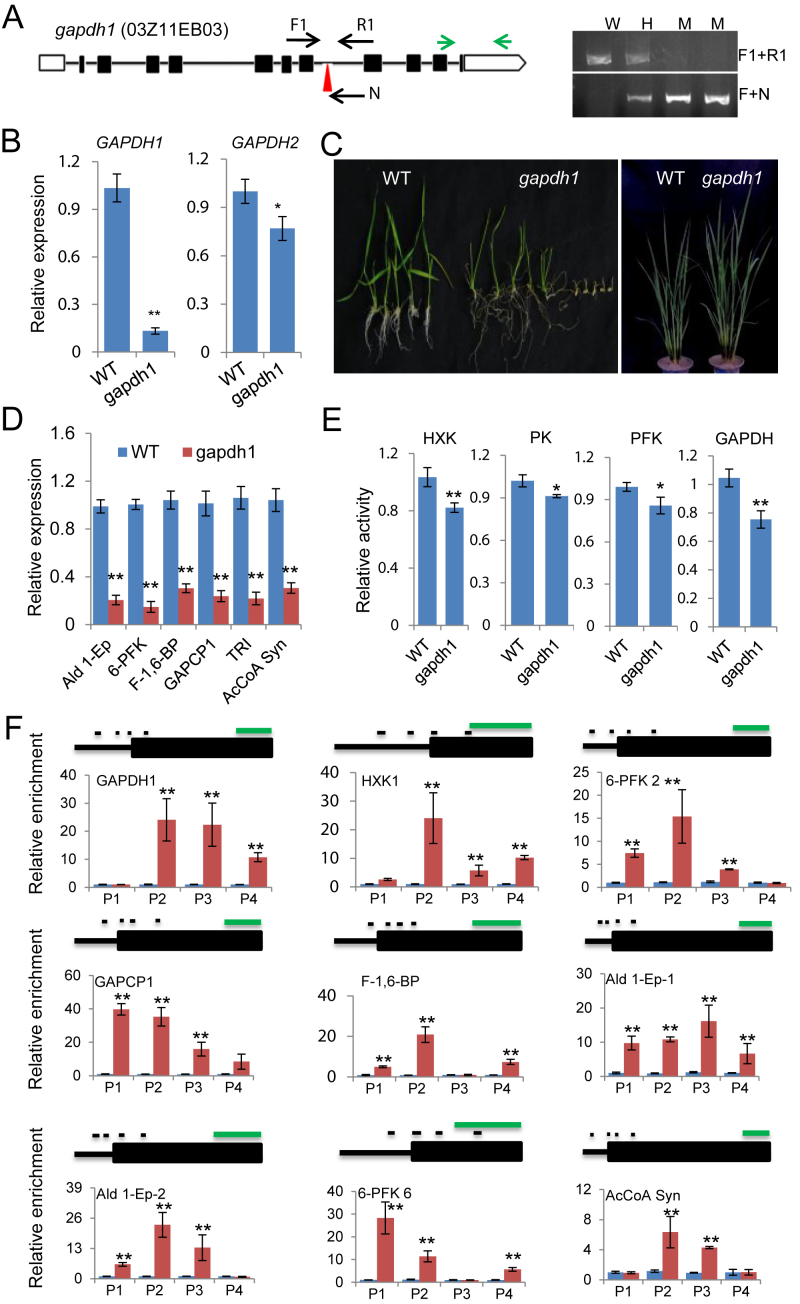
Figure 3.
OsGAPDH1 is required for glycolytic enzymes activity and gene expression. (A) Characterization of gapdh1 T-DNA mutant line. Left, Schematic representation of the OsGAPDH1 locus. The T-DNA insertion position in the seventh intron is indicated by red arrow head. The positions of primers F1, R1, and N used for genotyping are indicated. OsGAPDH1 specific primers used for RT-PCR are indicated by green arrows. Right, Genotyping of the gapdh1 T-DNA insertion. W, wild type; H, heterozygosis; M, homozygote. (B) Detection of OsGAPDH1/2 transcripts level in gapdh1. (C) The gapdh1 mutant phenotypes at seedling and maturation stages. (D) Transcript levels of glycolytic genes (Ald 1-Ep, 6-PFK, F-1,6-BP, GAPCP-1, TRI and AcCoA Syn). Actin1 was used as an internal control. (E) Glycolytic enzyme activities in the gapdh1 mutant relative to wild type. (F) OsGAPDH1 associated directly with the glycolytic genes. ChIP-qPCR assays were performed with seedling chromatin fragments of OsGAPDH-GFP plants using anti-GFP and anti-IgG, respectively. Small black lines indicate the relative positions of the primer sets P1 to P4 (left to right). Green line = 1 kb. Anti-IgG was used as controls. Bars in qRT-PCR, enzymatic activities, and ChIP-PCR are means ± SD from three biological replicates. Each replicate was performed using independently cultured plants. Significant enrichments (t test) calculated from three biological replicates are indicated (*P value < 0.05, **P value < 0.01).