Fig. 4.
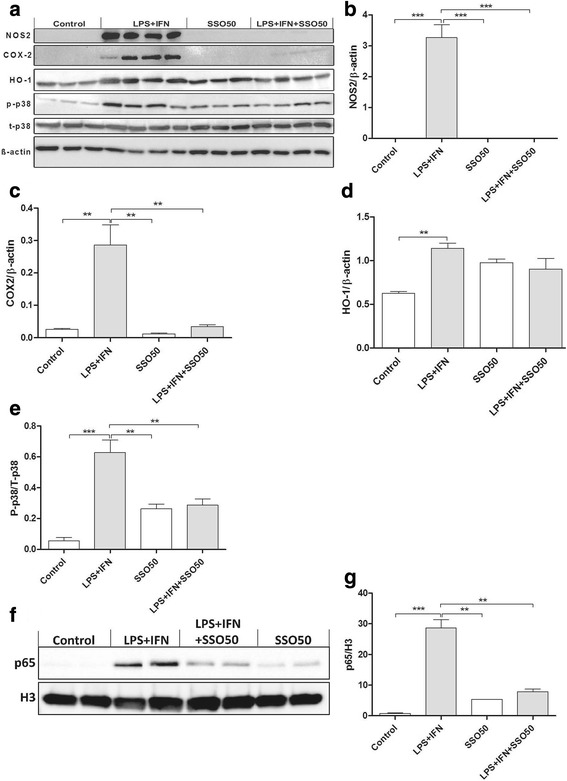
SSO reduces the protein levels of activated p38, iNOS, and COX-2 in vitro. BV2 cells were exposed to 100 ng/ml of LPS and 5 ng/ml of IFNγ in the presence or absence of 50 μM SSO. Figure (a) shows the representative images of Western blots probed for NOS2, COX-2, HO-1, p-p38, t-p38, and β-actin as control. Stimulation of BV2 cells with LPS/IFNγ for 24 h drastically increased the levels of NOS2 (b), COX-2 (c), HO-1 (d), and P-p38/T-p38 (e). Representative image of nuclear NFκB p65 translocation after nuclear fractionation. Nuclear-specific marker H3 was used to normalize p65 translocation (f). LPS/IFNγ stimulation resulted in robust nuclear translocation of NFκB p65, which was significantly prevented by SSO co-treatment (g). The results were analyzed with one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. n = 3-4 per group from independent experiments. *p < 0.01, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001
