Figure 1.
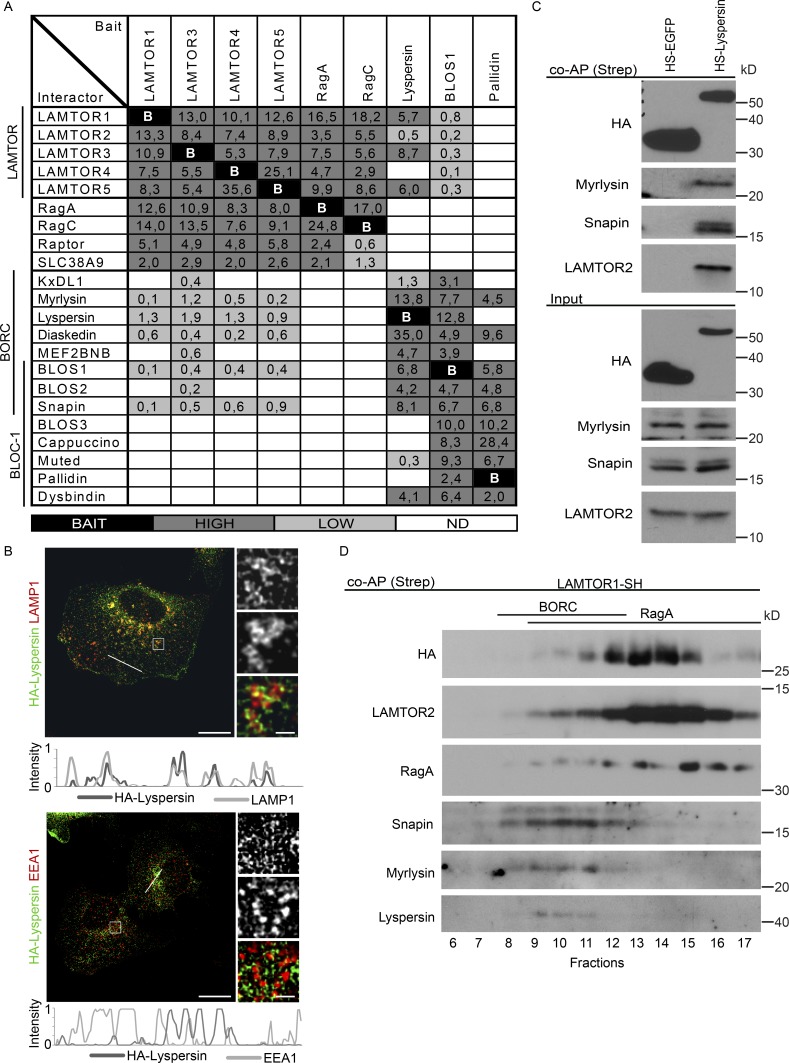
The LAMTOR pentamer participates in two distinct multimeric complexes on late endosomes/lysosomes. (A) Interactome analysis identifies two LAMTOR populations associating either with RagA/C, SLC38A9, and Raptor or with BORC. HS-tagged baits (LAMTOR1, LAMTOR3, LAMTOR4, LAMTOR5, RagA, RagC, lyspersin, BLOS1, and pallidin) were purified by TAP and analyzed by LC-MS/MS. The normalized abundances (% of total spectral counts [for LAMTOR 1, 3, 4, and 5, RagA, RagC, and BLOS1] or peak areas [for lyspersin and pallidin]) of the interacting partners are shown (Table S1). BAIT (black), bait; HIGH (dark gray), high abundance interactors (≥2%); LOW (bright gray), low abundance interactors (<2%); ND (white), no interaction detected. (B) HA-lyspersin partially colocalizes with late endosomes/lysosomes (LAMP1) but not with early endosomes (EEA1). HeLa cells were transfected with HA-lyspersin. Single plane confocal images of indirect IF of HA-lyspersin (green) and endogenous endosomal markers (red) are shown. Intensity profiles for HA-lyspersin (green) and LAMP1 or EEA1 (red) along the cross section lines are shown. Representative images are shown. Bars: 10 µm; (insets) 1 µm. (C) Immunoblotting analysis of HS-lyspersin Strep-purified complexes confirms the interaction of lyspersin with myrlysin, snapin, and LAMTOR2. (D) The majority of the pentameric LAMTOR complex associates with RagA. Only a minor fraction interacts with BORC components. The eluate from Strep-purified LAMTOR1-SH was subjected to size exclusion chromatography and analyzed by WB with the indicated antibodies.