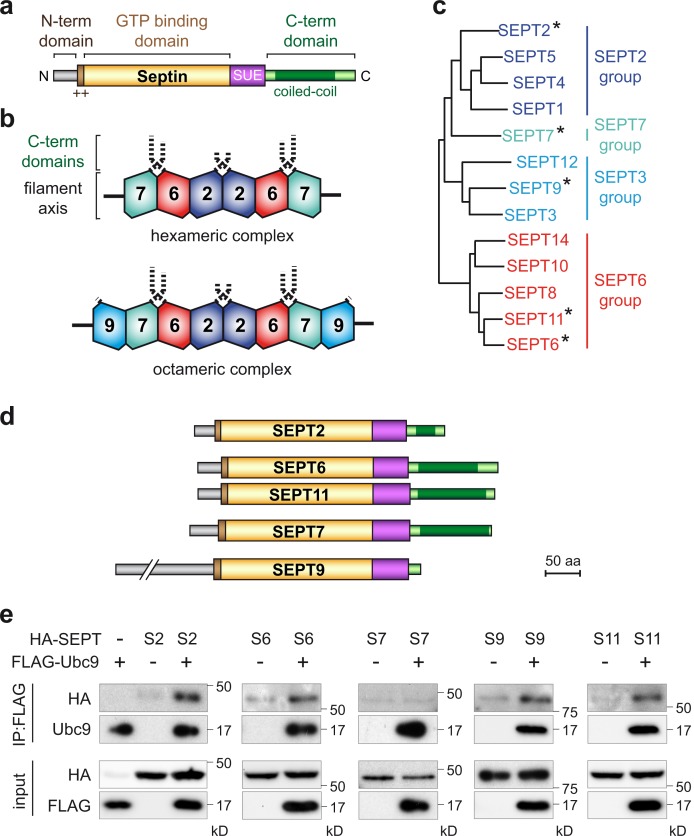
Figure 1.
Interaction between septins and the human SUMOylation machinery. (a) Schematic representation of a prototypical human septin protein (++, phosphoinositide-binding polybasic region; SUE, septin unique element). (b) Schematic organization of typical hexameric and octameric septin complexes. Dashed lines represent extensions formed by septin C-terminal domains. (c) Phylogenetic tree of human septins clustering into four different groups (asterisks denote septins analyzed in this study). (d) Schematic representation of the five human septins analyzed in this study. (e) HeLa cells were cotransfected with HA-tagged septins and FLAG-tagged Ubc9. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) using anti-FLAG antibodies, and coimmunoprecipitation of septins was assayed by immunoblot analysis using anti-HA, anti-FLAG, and anti-Ubc9 antibodies (S2, SEPT2; S6, SEPT6; S7, SEPT7; S9, SEPT9; S11, SEPT11).