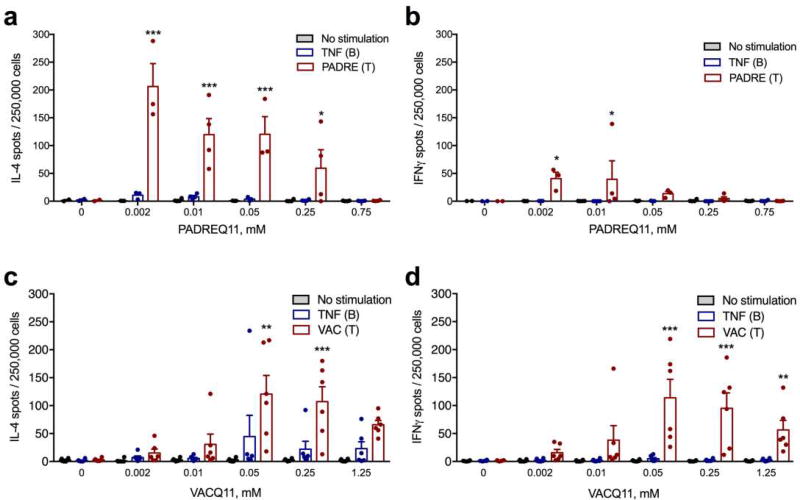
Figure 4. Co-assembled nanofibers elicited dose-dependent T-cell responses focused on the foreign CD4+ T-cell epitope, not the TNF B-cell epitope.
Cytokine-secreting cells from mice immunized with TNFQ11 combined with the indicated doses of T-cell epitope (PADREQ11 or VACQ11) were quantified ex vivo by ELISPOT after re-stimulation of lymph node cell suspensions with peptide TNF, peptide PADRE (a, b) or peptide VAC (c, d). In a–b, for the various PADREQ11 contents (0, 0.002, 0.01, 0.05, 0.25, and 0.75 mM) group sizes were 2, 3, 4, 3, 4, and 4 mice, respectively. c–d represent a combination of two independently conducted experiments, where sample sizes for each group were 3 mice (data in the figure shows these two experiments together, with a total sample size of 6 mice per group). Mean ± SD is shown. Statistical significance was tested by two way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Significance found between T and B-cell epitope stimulation at each T-cell epitope concentration is denoted. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.