Fig. 2.
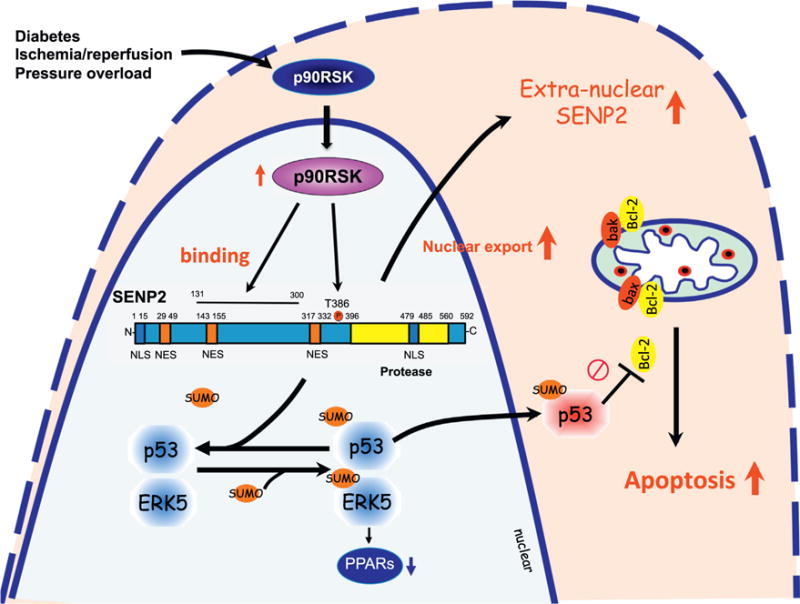
SENP2 shuttling between the nuclear and extra-nuclear compartments: SENP2 contains a bipartite nuclear localization signal (NLS) sequence at the N terminus domain and a leucine-rich, CRM1-dependent nuclear export signal (NES) sequence in the central region. These NLS and NES sequences are involved in SENP2 shuttling between the nucleus and the cytoplasm, which regulates levels of SUMOylation of proteins in these compartments. Activated p90RSK associates with SENP2, and phosphorylates T368 site, leading to SENP2 nuclear export. This nuclear export diminishes the nuclear SENP2 de-SUMOylation function in the nucleus, and consequently up-regulates SUMOylation of p53 and ERK5in the nucleus. p53 SUMOylation increases p53 nuclear export and binds with Bcl-2 in the cytoplasm, which inhibits Bcl-2 anti-apoptotic effects, and induces apoptosis. ERK5 SUMOylation inhibits transcriptional activity of PPARs, which can be detrimental to regulating the cardiac function and remodeling after cardiac insult.
