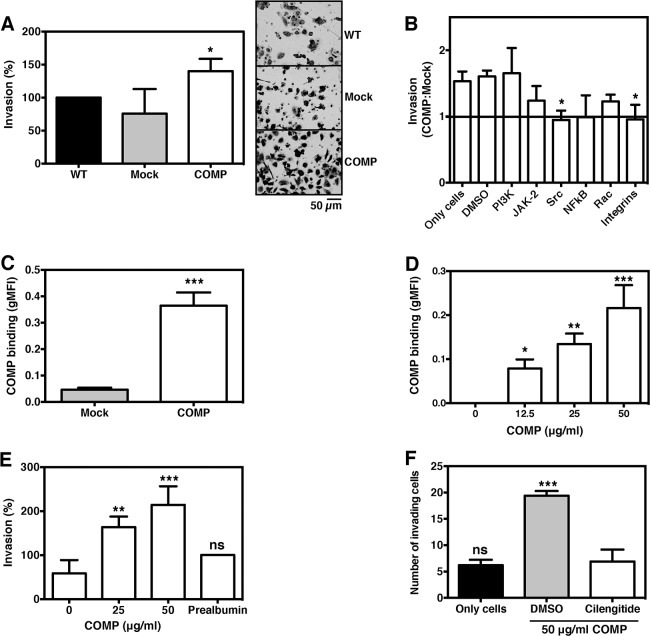
Figure 4. COMP drives the invasion of prostate cancer cells.
COMP-expressing cells are more invasive as compared to mock-transfected cells (A). The increased invasiveness was abolished after inhibition of Src or integrin signalling pathways (B). Since secreted COMP binds back to the surface of the transfected cells (C) and recombinant COMP binds mock-transfected cells in a dose-dependent manner (D), we investigated whether extracellular COMP can drive invasion. Indeed, recombinant COMP enhanced the invasion of mock-transfected cells dose dependently (E), and this effect was neutralized by inhibiting integrin signalling with Cilengitide (F). The data represent at least three independent experiments ±SD. Statistical differences were calculated with 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison test (A-B, D-F) or 2-tailed student's t-test (C). The symbols ns, *, **, and *** represent not significant, p < 0.05, p < 0.005 and p < 0.001, respectively.