Figure 7.
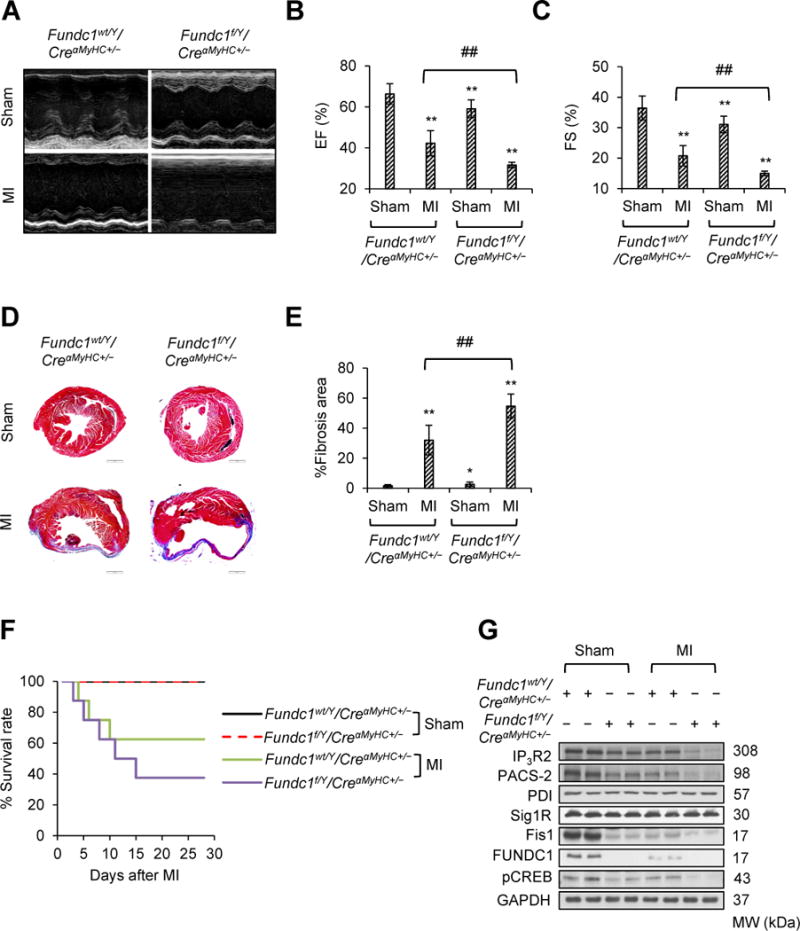
Acute myocardial infarction (MI) exacerbates cardiac dysfunction in cardiac Fundc1 knockout mice. Fundc1wt/Y/CreαMyHC+/− and Fundc1f/Y/CreαMyHC+/− mice were subjected to left anterior descending coronary artery ligation (MI) or sham surgery. Four weeks after surgery, cardiac structure and function were evaluated. A, Representative images of M-mode echocardiograms of Fundc1wt/Y/CreαMyHC+/− and Fundc1f/Y/CreαMyHC+/− mice subjected to MI or sham operation. The ejection fraction (EF) (B) and fractional shortening (FS) (C) are shown for each group (n = 8 mice per group, **P < 0.01 versus Fundc1wt/Y/CreαMyHC+/− & Sham; ##P < 0.01 versus indicated group). D, Representative images show Masson’s trichrome staining of the cardiac tissues. Scale bars, 1 mm. E, Quantitative analyses of the left ventricular fibrotic area in each group (n = 8 mice per group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus Fundc1wt/Y/CreαMyHC+/− & Sham; ##P < 0.01 versus indicated group). F, Kaplan-Meier curves of Fundc1wt/Y/CreαMyHC+/− and Fundc1f/Y/CreαMyHC+/− mice subjected to MI or sham operation (n = 8 mice per group). G, Protein levels of FUNDC1, phosphorylated cAMP response element binding protein (pCREB), inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate type 2 receptor (IP3R2), phosphofurin acidic cluster sorting protein 2 (PACS-2), protein disulfide isomerase (PDI), and sigma-1 receptor (Sig1R), and mitochondrial fission 1 protein (Fis1) in hearts were assayed by western blot.
