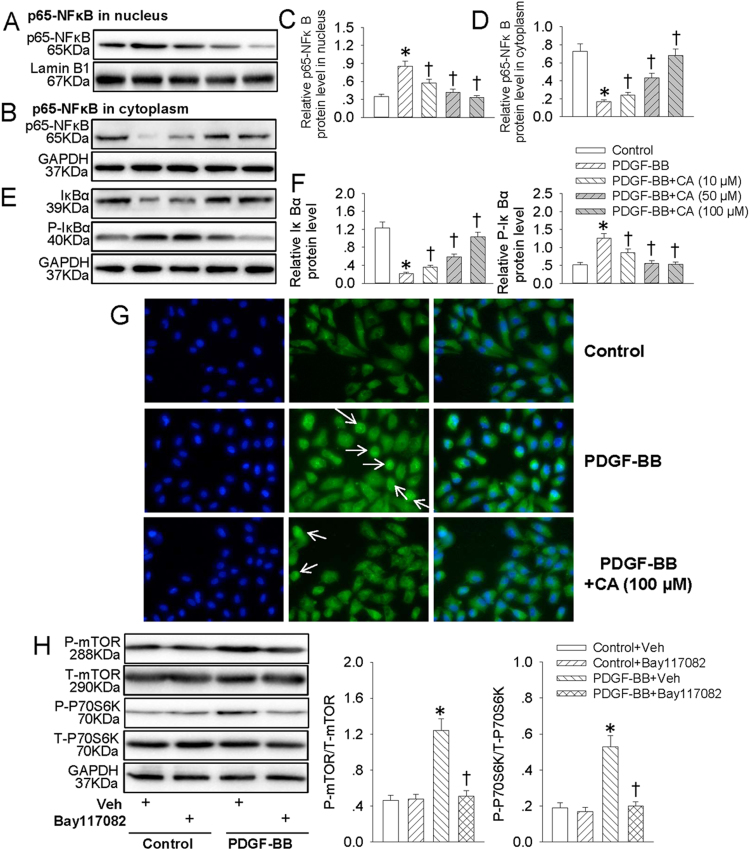
Fig. 5.
CA retarded PDGF-BB-induced NFκB signaling activation. VSMCs were pretreated with various concentrations (10, 50 and 100 μM) of CA for 6 h followed by stimulation with PDGF-BB (20 ng/mL) for 24 h. (A) Represented images showing the protein expressions of p65-NFκB in nucleus. (B) Represented images showing the protein expressions of p65-NFκB in cytoplasm. (C) Bar graph showing the relative protein expressions of p65-NFκB in nucleus. (D) Bar graph showing the relative protein expressions of p65-NFκB in cytoplasm. (E) Represented images showing the protein expressions of IκBα and phosphorylated IκBα. (F) Bar graph showing the relative protein expressions of IκBα and phosphorylated IκBα. (G) The translocation of p65-NFκB from cytoplasm to nucleus was measure by immunofluorescence, white arrow showing the nuclear localization of p65-NFκB. (H) VSMCs were pretreated with Bay117082 (10 μM) for 6 h followed by stimulation with PDGF-BB (20 ng/mL) for 24 h. The phosphorylated and total mTOR and P70S6K protein levels were measure by western blot. Values are mean ± SE. * P < 0.05 vs. Control or Control + Vehicle (Veh), † P < 0.05 vs. PDGF-BB or PDGF-BB + Vehicle (Veh). n = 6 for each group.