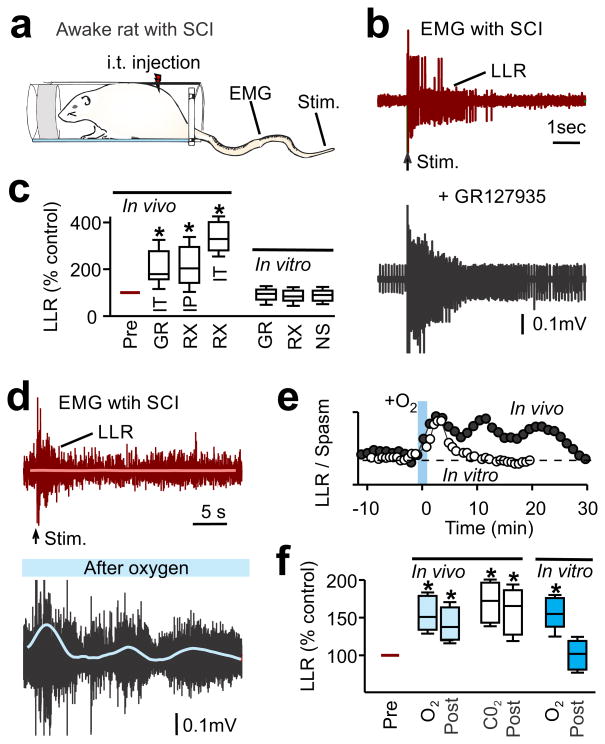
Figure 4.
Treatments that dilate vessels and improve oxygenation after SCI lead to increased motor activity. (a) Schematic of awake chronic spinal rat in Plexiglas bottle for tail muscle EMG recording and electrical stimulation of the tip of the tail (50×T) to evoke reflexes. (b) Representative muscle activity in a chronic spinal rat, showing baseline EMG activity prior to stimulation (arrow) and long-lasting reflex (LLR) evoked by stimulation, before (top) and after GR127935 treatment (bottom) (intrathecal [i.t.], 30 μl, 10 mM). (c) Box plots of the change in the LLR measured in vitro (rectified-average) induced by blocking the TA-mediated vasoconstriction of capillary flow with either GR127935 (GR, i.p. 8 mg/kg, n = 3 or i.t. 10 mM in 30 μl; n = 2; combined) or RX821002 (RX, i.p. 1 mg/kg, n = 11; or i.t. 3 mM in 30 μl, n = 5), and compared to the change in LLR studied in the isolated in vitro spinal cord, with application of GR127935 (3 μM, n = 18), RX821002 (1 μM, n = 42) and NSD1015 (NS, 300 μM, n = 9) (see Supplementary-Fig-15). LLR normalized to LLR prior to drugs, 100%. (d) Representative EMG trace in a chronic spinal rat before and 15 min after transient breathing of 95% O2 (1 min, with 5% CO2). Smoothed rectified rhythmic activity is indicated by the blue line. (e) Time course of mean LLR before and after transiently increased O2 breathing in vivo (1 min), compared to LLR response to increased O2 in the isolated in vitro spinal cord (pO2 increased in nACSF). (f) Box plots of LLR in injured rats in vivo, either prior to treatment (Pre), during treatment with O2 or CO2, or 10–20 min post-treatment (post). Treatments were transient hyperoxia (O2, 95% for 1 min, n = 8) or hypercapnia (CO2, 10% in air for 30 sec, n = 10) breathing. Also shown are data for in vitro isolated spinal cords during or after treatment with O2 (n = 6). All conditions normalized as in c. * P < 0.05 significant difference relative to pre-drug condition.