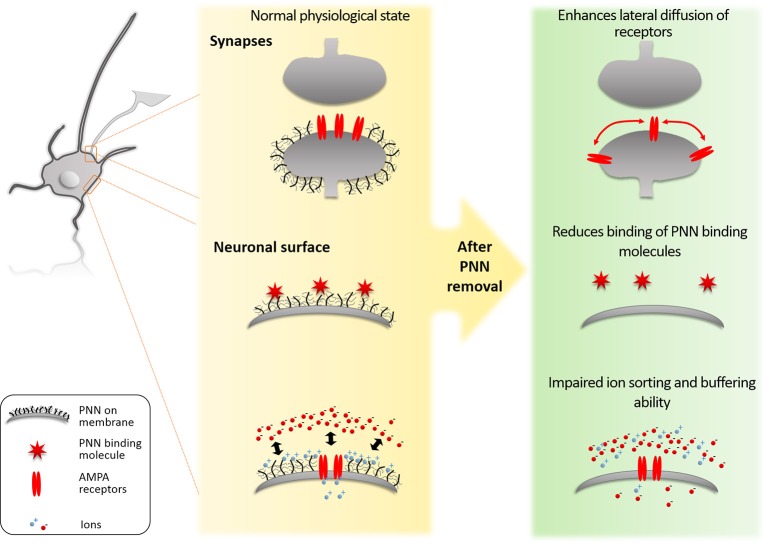
Figure 1.
Molecular mechanisms of PNNs. (1) The PNNs block lateral diffusion of membrane bound proteins such as AMPA receptors. By this mechanism the PNNs limit synaptic plasticity. (2) The PNNs bind specifically to proteins such as Sema3A and Otx2. This binding regulates which ECM proteins can reach the PNN neuron and also present these proteins on its surface to signal to approaching axons from other neurons. (3) The PNNs act as a physical barrier for ion sorting and buffering on the neuronal surface. The high negative charge of the PNNs repels anionic ions/molecules (such as reactive oxygen) to reach the neuronal surface, while it attracts the cationic ions/molecules and creates a reservoir for fast buffering of ions required for the synaptic function and to prevent oxidative stress induced by Fe3+.