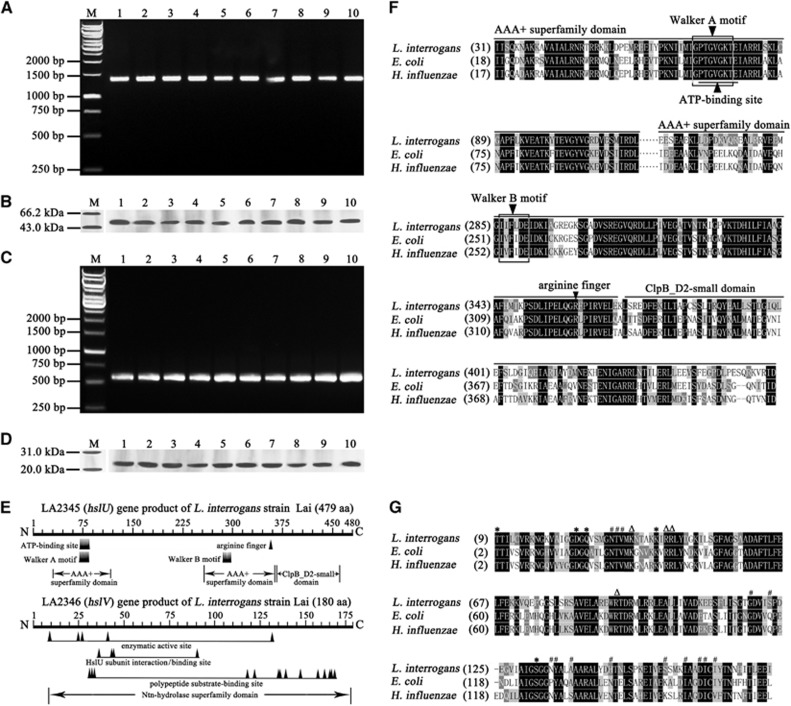
Figure 1.
Extensive distribution and expression of hslU and hslV genes in L. interrogans strains and analysis data of AAA+ chaperone–peptidase complex domains. (A) The hslU gene segments amplified from different L. interrogans strains by PCR. Lane M: DNA marker. Lanes 1–10: amplicons of the hslU genes from L. interrogans serogroup Icterohaemorrhagiae serovar Lai strain Lai; serogroup Canicola serovar Canicola strain Lin; serogroup Pyrogenes serovar Pyrogenes strain Tian; serogrouop Autumnalis serovar Autumnalis strain Lin4; serogroup Australis serovar Australis strain 65-9; serogroup Pomona serovar Pomona strain Luo; serogroup Grippotyphosa serovar Grippotyphosa strain Lin6; serogroup Hebdomadis serovar Hebdomadis strain 56069; serogroup Bataviae serovar Paidjan strain L37; and serogroup Sejroe serovar Wolffi strain L183, respectively. (B) The HslU proteins from different L. interrogans strains detected by western blot assay. Lane M: protein marker. The legend for the lanes 1–10 is the same as in A but for the HslU protein detection. (C) The hslV gene segments amplified from different L. interrogans strains by PCR. The legend for the lanes M and 1–10 is the same as in A but for the hslV gene detection. (D) The HslV proteins from different L. interrogans strains detected by western blot assay. Lane M: protein marker. The legend for the lanes 1–10 is the same as in A but for the HslV protein detection. (E) Predictive chaperone and peptidase domains in the HslU and HslV from L. interrogans strain Lai. The Walker A and B motifs function as nucleotide phosphate- and Mg2+-binding sites, respectively. The arginine finger is responsible for sensing ATP binding and hydrolysis and conformational change. (F) Comparison of domains in HslU proteins from L. interrogans, E. coli and H. influenzae. (G) Comparison of domains in HslV proteins from L. interrogans, E. coli and H. influenzae. ‘*’, ‘#’ and ‘Δ’ indicate the enzymatic active, polypeptide substrate-binding and HslU subunit interaction sites, respectively.