Figure 9.
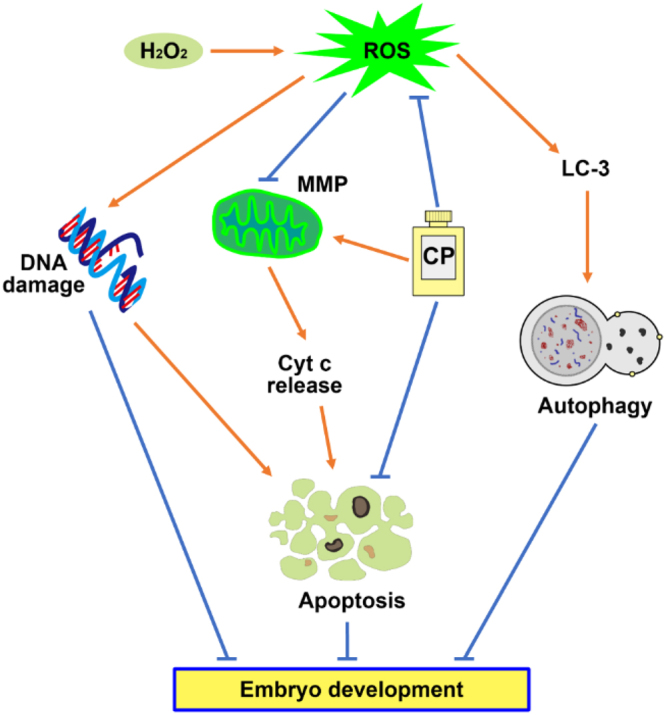
Schematic representation of the protective effect of CP during porcine embryonic development. H2O2 exposure causes the generation of oxidative stress, resulting in DNA damage, autophagy, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Apoptosis was induced by the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria because of the compromise of MMPs. Addition of CP promotes embryo development by attenuating H2O2-induced oxidative stress, apoptosis, and compromised MMP because of the antioxidative, anti-apoptosis, and protection mitochondrial dysfunction properties.
