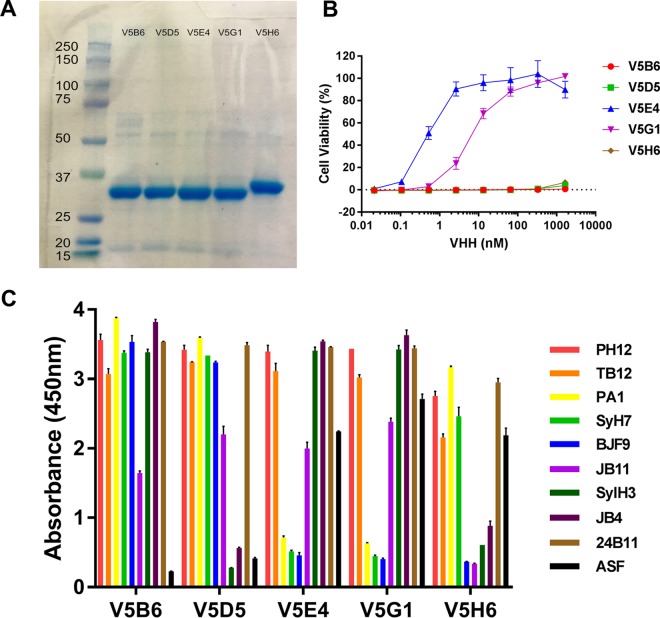
FIG 1.
Expression and characterization of ricin-specific VHHs. All 68 VHHs in this study (Table 2) were subjected to analysis by SDS-PAGE, toxin-neutralizing assays, and competition ELISA. Data shown here represent results of analysis of five representative RTB-specific VHHs: V5B6, V5D5, V5E4, V5G1, and V5H6. (A) VHHs were subjected to SDS-PAGE, and the resulting gel was stained with Coomassie blue. Molecular mass standards (with kilodalton notations) are shown in the far left lane. The major band (∼33 to ∼35 kDa) in each lane corresponds to the expected molecular mass of the recombinant VHHs, with an N-terminal thioredoxin fusion partner, a hexa-His tag, and a C-terminal epitope E-tag, as described in the supplemental methods. (B) Toxin-neutralizing activity, as determined in a Vero cell-based microtiter plate assay. The representative set of VHHs consists of two VHHs with strong TNA (IC50 = <10 nM) and three with no TNA. (C) Competition ELISA, as described in Materials and Methods. Microtiter plates were coated with the indicated MAbs or ASF (legend on right) and then overlaid with ricin. The plates were probed with VHHs, as indicated along the x axis, and were developed with anti-E-tag secondary antibodies. As such, the sandwich ELISA data provided relative competition values against a panel of RTA- and RTB-specific MAbs. The failure of the VHHs to recognize ricin toxin when bound to ASF is indicative of the antibodies recognizing epitopes near one of the RTB Gal/GalNAc binding sites. The full array of competition ELISAs is presented in Data Set S1.