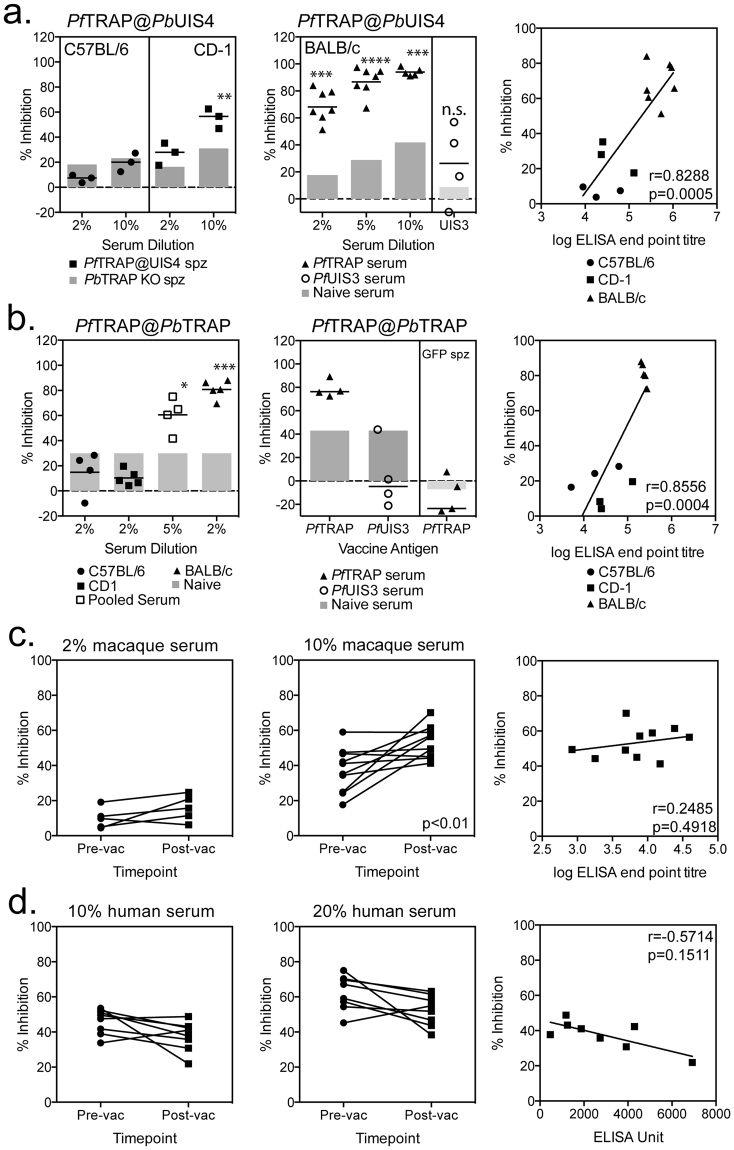
Figure 5.
Inhibition of PbPfTRAP sporozoite invasion with serum from PfTRAP vaccinated mice, macaques and humans. (a) C57BL/6, CD-1 or BALB/c mice immunised with 108 iu ChAd63-PfTRAP and boosted with 106 pfu MVA-PfTRAP (C57BL/6 or CD-1) or 107 pfu MVA-PfTRAP (BALB/c) at least 6 weeks later, with serum harvested approximately 2 weeks after the MVA boost. In a separate experiment, BALB/c mice vaccinated with 108 iu ChAd63-PfUIS3 and boosted with 107 pfu MVA-PfUIS3 were used as an irrelevant antigen control (middle). Huh7 cells were infected with PfTRAP@PbUIS4 sporozoites mixed with increasing concentrations of serum prior to harvesting cells to determine P. berghei infectivity by flow cytometry 24 to 28 hours later. Graphs represent the percentage of inhibition observed with serum samples from C57BL/6 and CD-1 (left) or BALB/c (middle) vaccinated mice, grey bars denote the level of inhibition observed with naïve serum or inhibition observed against P. berghei that does not express PbTRAP (left). Data in each graph was analysed with a two-way ANOVA and post-hoc Sidaks multiple comparison, asterisk denote the level of significance comparing PfTRAP samples against naïve serum samples, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Inhibition of 2% serum samples plotted against the level of PfTRAP specific antibodies measured by endpoint ELISA (right) with data analysed with a Spearmans non-parametric correlation test, a significant positive correlation was observed (p = 0.0005). (b) C57BL/6, CD-1 or BALB/c mice immunised with 108 iu ChAd63-PfTRAP and boosted with 106 pfu MVA-PfTRAP (C57BL/6 or CD-1) or 107 pfu MVA-PfTRAP (BALB/c) at least 6 weeks later, with serum harvested approximately 2 weeks after the MVA boost. BALB/c mice vaccinated with 108 iu ChAd63-PfUIS3 and boosted with 107 pfu MVA-PfUIS3 were used as an irrelevant antigen control (middle). Huh7 cells were infected with PfTRAP@PbUIS4 or GFP only (middle) sporozoites and cells harvested between 24 and 28 hours later to determine P. berghei infectivity by flow cytometry. Graphs represent the percentage of inhibition observed with serum samples from C57BL/6 and CD-1 or BALB/c (left) vaccinated mice, grey bars denote the level of inhibition observed with naïve serum. Inhibition of 2% serum samples plotted against the level of PfTRAP specific antibodies measured by endpoint ELISA (right) with data analysed with a Spearmans non-parametric correlation test, a significant positive correlation was observed (p = 0.0004). Data in each graph was analysed with a two-way ANOVA and post-hoc Sidaks multiple comparison, asterisk denote the level of significance comparing PfTRAP samples against naïve serum samples, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. (c) Rhesus macaques were vaccinated with ChAd63.ME-TRAP followed 8 weeks later by an MVA.ME-TRAP boost were tested for the ability to inhibit invasion of Huh7 cells by PfTRAP@PbUIS4 sporozoites in the standard ISI assay. Pre-vaccination (circle) and 3 week post-MVA boost (square) serum samples were tested at 2% (left) and 10% (middle) serum dilutions, with % inhibition of 10% serum samples (right) compared to the level of post-vaccination TRAP specific antibodies measured by ELISA (right). Data was analysed with a non-parametric Spearmans correlation test, but no significant correlation was observed. (d) Serum samples from human volunteers vaccinated with a ChAd63.ME-TRAP followed by MVA.ME-TRAP were tested in the ISI assay for the ability to inhibit the invasion of Huh7 cells with PfTRAP@PbUIS4 sporozoites. Pre-vaccination (circle) and 2 to 3 week post MVA boost (square) boost serum samples were tested at 10% (left) and 20% (middle) serum concentrations and the percentage of inhibition compared to the level of TRAP specific antibodies measured by ELISA (right) with data analysed with a non-parametric Spearmans test, but no significant correlation was observed.