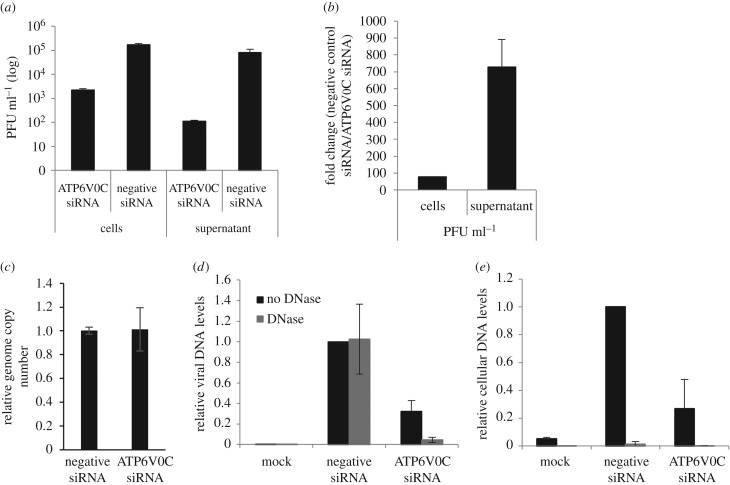
Figure 1.
Knockdown of ATP6V0C has greater effect on supernatant virus than cell associated virus. Fibroblast cells were transfected with siRNA against ATP6V0C or a control siRNA and infected with TB40/E-GFP at an MOI of 1 and cells and supernatant collected 7 days post-infection. (a) Infectious cell associated and supernatant virus levels were determined by dilution plaque assay following ATP6V0C knockdown. (b) Effects of ATP6V0C knockdown on infectious supernatant virus levels are greater than effects on cell associated virus. (c) Cell associated viral genome levels were equivalent between control cells and ATP6V0C knockdown cells at 7 days post-infection (d) Supernatant virion genome levels were determined by qPCR. Supernatant was collected from cells 7 days post infection. Virions were isolated from supernatant by ultracentrifugation then treated with DNase to degrade non-virion associated viral DNA. Primers against HCMV gB were used to determine viral genome levels and primers to GAPDH (e) were used to confirm successful degradation of non-protected DNA (n = 2).