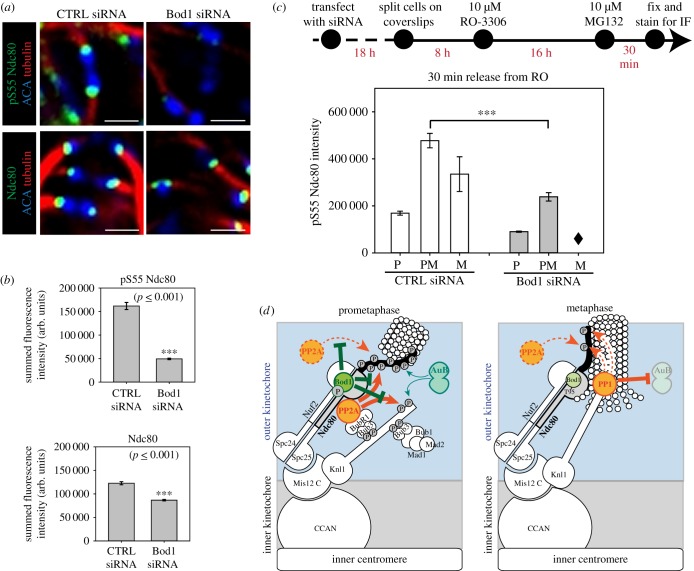
Figure 7.
Bod1 depletion interferes with phosphorylation of the Ndc80 N-terminal tail. (a) HeLa cells were treated with control or Bod1 siRNA for 48 h, fixed in paraformaldehyde and stained with a phospho-specific antibody against a phosphoepitope (pS55) in the Ndc80 N-terminal tail, or a total Ndc80 antibody. Metaphase cells or cells with the characteristic Bod1 chromosome misalignment phenotype were imaged. Kinetochores of chromosomes on the metaphase plate within a single z-plane are shown. Scale bars are 1 µm. (b) pS55 and total Ndc80 intensities at kinetochores were quantified. Pairwise comparisons were evaluated by unpaired Student's t-test. Two-tailed p-values are shown. n = 10 cells per condition. Error bars represent standard error. (c) Timeline and quantification of treatments to compare kinetics of Ndc80 phosphorylation in control and Bod1-depleted HeLa cells in early mitosis. Twenty-six hours after transfection, cells were synchronized at G2/M transition with the Cdk1 inhibitor RO-3306 for 16 h. They were then released into culture medium containing the proteasome inhibitor MG132 to prevent mitotic exit and fixed 30 min after their release from G2/M arrest. pS55 Ndc80 fluorescence intensities at kinetochores of mitotic cells were quantified. n = 50 mitotic cells per condition. Three asterisks indicate high significance in pairwise multiple comparison after ANOVA on ranks (p < 0.001). Diamond indicates that no quantification could be performed for metaphase pS55 Ndc80 in Bod1 siRNA-treated cells, because lack of Bod1 caused a significant delay in early mitotic progression leading to the absence of metaphase cells 30 min after release from RO-3306. (d) A model integrating data presented in this paper with previous findings on the temporal regulation of kinetochore phosphatases in mitosis. Bod1 phosphorylation in early mitosis can inhibit PP2A-B56 activity [9] and prevent premature dephosphorylation of Ndc80 at its N-terminus and Knl1 at the SILK, RVSF and MELT motifs. Dephosphorylation of Bod1 in later stages by an unknown mechanism, coincides with increased PP2A activity and recruitment of PP1. PP2A, bound at an unidentified site within the kinetochore, and PP1 are free to dephosphorylate kinetochore epitopes and inhibit Aurora B activity in metaphase [12–14,48–50]. Dashed lines indicate implied activity but no direct evidence.