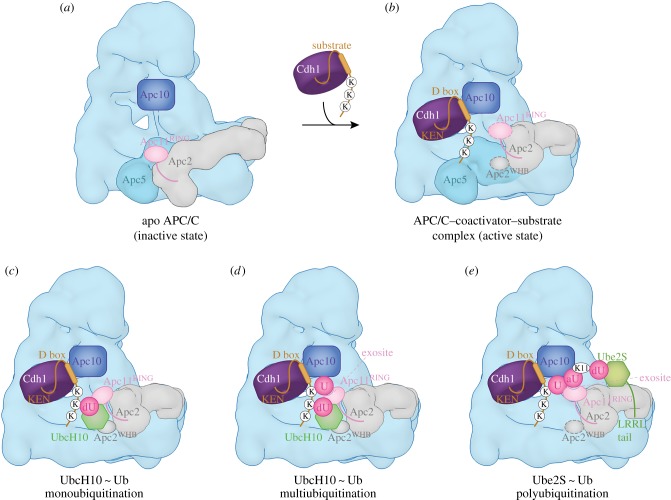
Figure 7.
Schematic of ubiquitination reaction catalysed by the APC/C. (a) In the apo state, the downward position of the catalytic module would cause a clash between Apc5 and both UbcH10 and Apc2WHB (as in the APC/CCdh1.substrate–UbcH10 ∼ ubiquitin complex). (b) Binding of coactivator shifts the catalytic module (Apc2 and Apc11) to an upward position. Apc2CTD together with Apc2WHB and Apc11RING are highly flexible. Target lysines on the APC/C substrate are shown as ‘K’. (c) UbcH10-catalysed monoubiquitination. dU: UbcH10-conjugated donor ubiquitin. Apc2WHB rigidifies by binding to UbcH10, Apc11RING is less flexible. (d) UbcH10-catalysed multiubiquitination. The substrate-conjugated ubiquitin (U) engages the ubiquitin-binding exosite of Apc11RING. (e) Ube2S-catalysed polyubiquitination. The distal acceptor ubiquitin (aU) of the polyubiquitin chain engages the ubiquitin-binding exosite of Apc11RING positioning Lys 11 adjacent to the catalytic site of Ube2S. dU: donor ubiquitin conjugated to Ube2S. Dashed lines around Apc11RING and Apc2WHB denote conformational flexibility. Based on schemes from Brown et al. [112] and Chang & Barford [162].