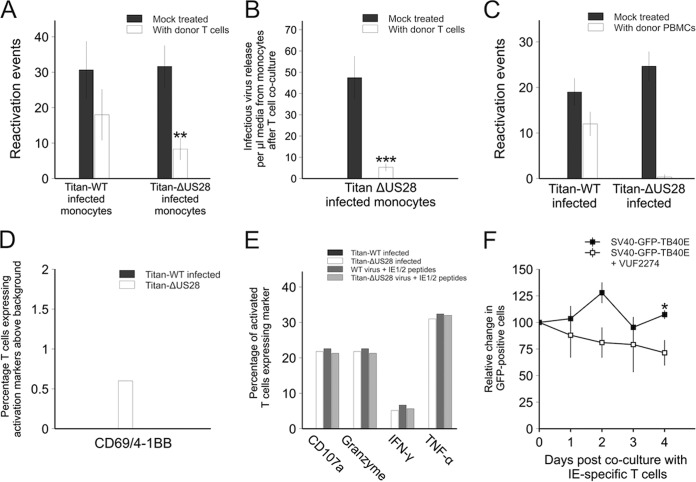
FIG 10 .
Monocytes infected with Titan-ΔUS28 or monocytes infected with SV40-GFP-TB40E in the presence of US28 inhibitors are targets for HCMV-specific T cell responses. (A) CD14+ monocytes were infected with either Titan-WT or Titan-ΔUS28. Three days postinfection, monocytes were cocultured with IE72-specific T cells for a further 3 days. After this, monocytes were washed to remove T cells and monocytes were then differentiated and matured to induce virus reactivation. Reactivated virus was quantified by fibroblast coculture and staining for IE foci. (B) Monocytes were removed from media from the experiment described for panel A at 3 days after T cell treatment and titrated onto fibroblasts to quantify virus release from Titan-ΔUS28-infected monocytes. (C) CD14+ monocytes from seropositive donors were infected with either Titan-WT or Titan-ΔUS28, and the nonmonocyte PBMCs were added back to the infected monocytes 3 days postinfection for 4 days and then removed by washing. The remaining adherent monocytes were then differentiated and matured to induce virus reactivation. Reactivated virus was quantified by fibroblast coculture and staining for IE foci. (D) CD14+ monocytes from seropositive donors were infected with either Titan-WT or Titan-ΔUS28, and, 5 days postinfection, latent monocytes were left untreated or cocultured overnight with isolated CD8+ T cells from the same donor and analyzed for expression of the activation markers CD69 and 4-1BB and for expression of the following degranulation markers: CD107a; granzymes A, B, and K; TNF-α; and IFN-γ. Data in panel D represent the percentage of CD8+ T cells expressing both activation markers, above background stimulation levels, in response to either Titan-WT-infected or Titan-ΔUS28-infected monocytes. (E) The proportions of HCMV-specific CD8+ T cells expressing degranulation markers seen with those activated monocytes are shown, as are those of CD8+ T cells stimulated with virus-infected monocytes and pulsed with IE1/2 peptides as antigen-specific positive controls. (F) Monocytes from an HLA-A2-positive donor were latently infected with SV40-GFP-TB40E and were left untreated or treated with VUF2274 3 days postinfection. Two days posttreatment with drug, monocytes were cocultured with IE72-specific T cells, following which monocytes expressing GFP were counted over the subsequent 4 days. Data points for all panels show means of results from at least three independent experiments; error bars show standard deviations.