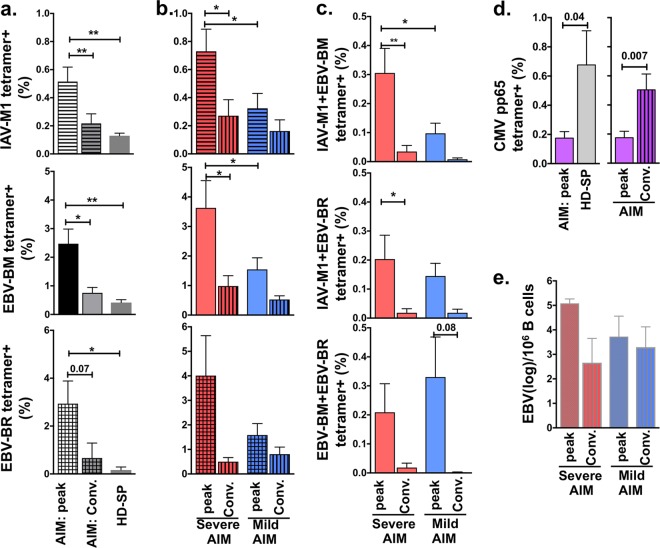
FIG 3 .
PBMCs in patients with severe AIM had a greater mean frequency of total IAV-M1, EBV-BM, and IAV-M1+EBV-BM tetramer+ CD8 T cells than mild-AIM patients (when analyzed ex vivo). (a) All AIM patients had a significantly higher mean peak frequency of total IAV-M1-, EBV-BM-, and EBV-BR-specific tetramer+ CD8 T cells than healthy persistently infected EBV-seropositive donors (HD-SP). (b) When patients were categorized into two groups on the basis of disease severity (see Materials and Methods), severe-AIM patients had a significantly higher mean peak frequency of total IAV-M1 and EBV-BM tetramer+ cells, but not EBV-BR, directly ex vivo in their PBMCs than mild-AIM patients (n = 8 to 22 donors per group). The ex vivo mean frequency of total IAV-M1 and EBV-BM tetramer+ cells significantly decreased from the peak to the convalescent (conv) phase in the severe-AIM group (n = 6 to 12 donors per group). (c) The mean peak frequency of IAV-M1+EBV-BM tetramer+ cells in severe-AIM patients was higher than that in mild-AIM patients but not that in the other two cross-reactive populations. (d) In CMV-seropositive donors, CMV pp65 tetramer+ CD8 T cells were lower in AIM patients than in HD-SP and higher in the convalescent phase than the peak CD8 T-cell responses during AIM (AIM patients, n = 11; convalescent [Conv.] AIM patients, n = 8; HD-SP, n = 11). (e) There was no significant difference in the mean peak or convalescent-phase EBV load (measured as the genome copy number [log] per 106 B cells) between severe- and mild-AIM patients. The Student t test was used to compare two groups, and one-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple-comparison test was used to compare more than two. Severe-AIM groups, red; mild-AIM groups, blue. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.