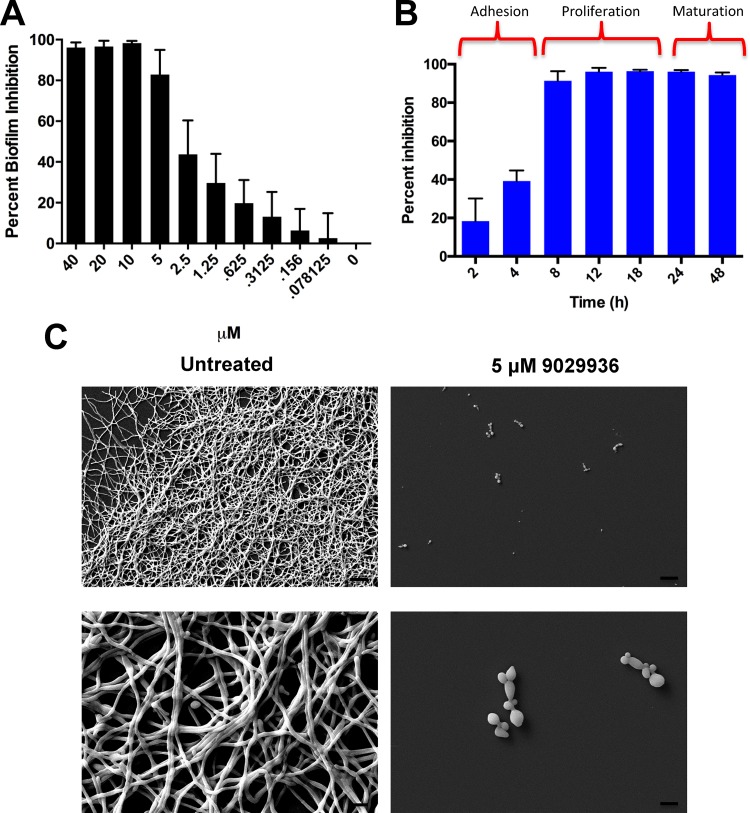
FIG 5 .
In vitro characterization of the inhibitory activity of the leading compound 9029936 on C. albicans biofilm formation. (A) Dose-dependent inhibitory effects of compound 9029936 on C. albicans biofilm formation. The compound was tested in serial 2-fold dilutions (concentrations ranging from 40 to 0.078 µM), with appropriate positive and negative controls. Results shown are the mean percent biofilm inhibition relative to control biofilms (grown in the absence of compound 9029936), determined in XTT colorimetric assays for multiple technical replicates from several independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviations. (B) The leading compound inhibited the proliferation and maturation phases of C. albicans biofilm development. A biofilm kinetic assay was performed in order to examine the inhibitory effects of compound 9029936 at different stages of biofilm development, using the same 96-well microtiter plate model of C. albicans biofilm formation. The extent of inhibition was determined at multiple times (2, 6, 8, 12, 24, and 48 h) after seeding the wells with C. albicans cells in the presence or absence of compound 9029936 (5 μM concentration). Results are expressed as means of multiple technical replicates from a single experiment, with error bars representing standard deviations. (C) SEM images of biofilms of C. albicans strain SC5314 formed in the absence or presence of compound 9029936 at a concentration of 5 μM. Bars, 20 μm.