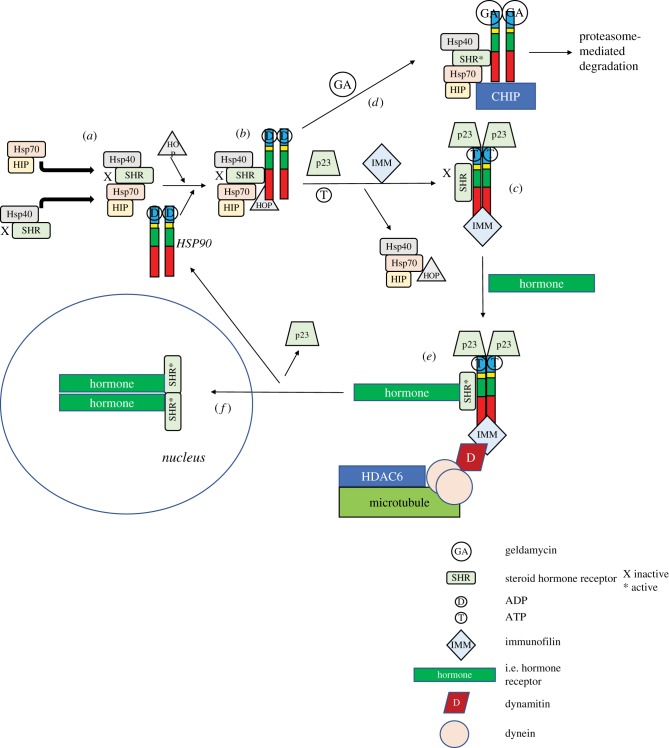
Figure 5.
HSP90-dependent steroid hormone receptor activation as an example of HSP90 activity. (a) The HSP90 complex is established by interactions of HSP70, HSP70-interacting protein (HIP), HSP40 and the steroid hormone receptor (SHR). (b) The SHR is transmitted via interaction with the HSP90 dimer to (c) associate with p23/IMM to change the HSP90 confirmation. Upon binding ATP, the immunophilins bind in place of the HSP70 and co-chaperones. (d) Binding of geldanamycin (a 1,4-benzoquinone ansamycin anti-tumour antibiotic that inhibits HSP90 function by binding to the ADP/ATP-binding pocket [81]) induces the disassociation of p23 and HOP, allowing the carboxyl terminus of HSC70-interacting protein (CHIP) ubiquitin ligase to attached to the complex, to poly-ubiquitinate and target it for proteasome-dependent degradation. (e) The HSP90–immunophilin–p23 complex activates SHR, which then binds steroid hormone, binds dynamitin and dynein (microtubule-associated proteins), which are then (f) trafficked along the cytoskeleton to the nucleus, where they dimerize and interact with the promoters of target genes. GA, geldamycin; SHR, steroid hormone receptor; D (in circle), ADP; T, ATP; IMM, immunofilin; D (in rhombus), dynamitin; peach circle, dynein. Adapted from [82].