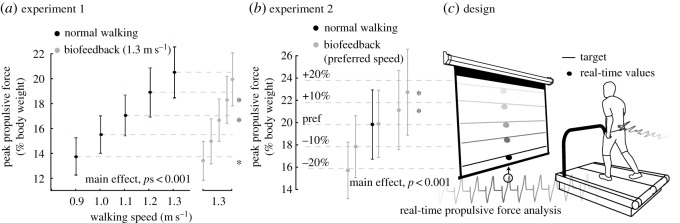
Figure 1.
Group mean (standard deviation) peak propulsive force values (a) when walking across a range of speeds and at 1.3 m s−1 with biofeedback of propulsive force targets extracted from slower speeds and (b) walking at preferred speed with propulsive forces ±10% and ±20% larger than preferred. (c) Experimental design using visual biofeedback of real-time propulsive force values calculated from a dual-belt, force-measuring treadmill to decouple the effects of walking speed and propulsive force generation on metrics of dynamic balance control. Asterisks represent significant (p < 0.05) difference from prescribed values.