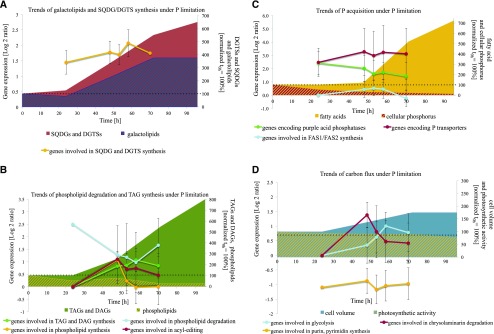
Figure 5.
Trends of cellular changes in −P cells of N. oceanica as a function of time. A, Changes of genes derived from microarray data involved in DGTS and SQDG synthesis (yellow line, one S-adenosyl-Met [AdoMet]:DAG 3-amino-3-carboxypropyltransferase [BTA], one UDP-sulfoquinovose synthase, one sulfolipid sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerol synthase), shown with changes of galactolipid (blue striped area) and SQDG/DGTS change (red area) normalized to time point 0 h. B, Changes of TAGs and DAGs (green area), phospholipids (yellow striped area) normalized to time point 0 h, and the expression of genes involved in phospholipid degradation (blue line; three glycerophosphoryl diester phosphodiesterases, two patatin-like phospholipases A, four phospholipases A, two lysophospholipases), acyl editing (red line; one lysophosphatidylglycerol acyltransferase, one cholinephosphotransferase, one phospholipid/diacylglycerol acyltransferase, two phospholipases D), TAG and DAG biosynthesis (green line; two glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferases, three lysophosphatidylglycerol acyltransferases, four phosphoesterase PA-phosphatases, eight diacylglycerol acyltransferases, one diacylglycerol kinase, one lipid droplet surface protein), and phospholipid biosynthesis (yellow line; one kinase, one ethanolamine phosphate cytidylyltransferase and phosphotransferase, one cholinephosphotransferase, one phosphoethanolamine N-methyltransferase, one CDP-diacylglycerol-inositol 3-phosphatidyltransferase). C, Changes of FA abundance (yellow area) and cellular P (red striped area) normalized to time point 0 h and of the expression of genes involved in P transporters (red line; five Pi transporters, two triose phosphate translocators, two vacuolar chaperone transporters), 10 purple acid phosphatases (green line), and FAS1/FAS2 synthesis (blue line; three acetyl-CoA carboxylases, two ketoacyl-synthases, three acyl-CoA synthetases, two long-chain acyl-synthetases, one thioesterase, two polyketide synthases type II, one peptide synthase, one hydroxyacyl-CoA synthase, six desaturases, two elongases). D, Changes of cell volume (blue area) and photosynthetic activity (yellow striped area) normalized to time point 0 h and the expression of genes involved in glycolysis (blue line; two Fru-2,6-bisphosphatases, two phosphoglycerate kinases, one glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, one dihydroxy-butanonkinase, one glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, four phosphoglycerate mutases, one enolase, three pyruvate kinases), chrysolaminarin degradation (red line; 11 endoglucanases, two exoglucanases), and purin, pyrimidine synthesis (yellow line). The presentation shows average log2 ratios of significantly expressed genes (P < 0.01) involved in metabolic clusters and changes of lipid classes (adjusted nmol 106 cells−1) or physiological parameters, such as cell volume (μm3) and FAs (pg cell−1) normalized to 0 h as 100%. For gene identifiers used for the calculation of average gene regulation and means, see Supplemental Excel Sheet S1. Average values ± se of the regulation of genes (P > 0.01 at each specific time point) involved in the specific pathway/catalysis are shown.