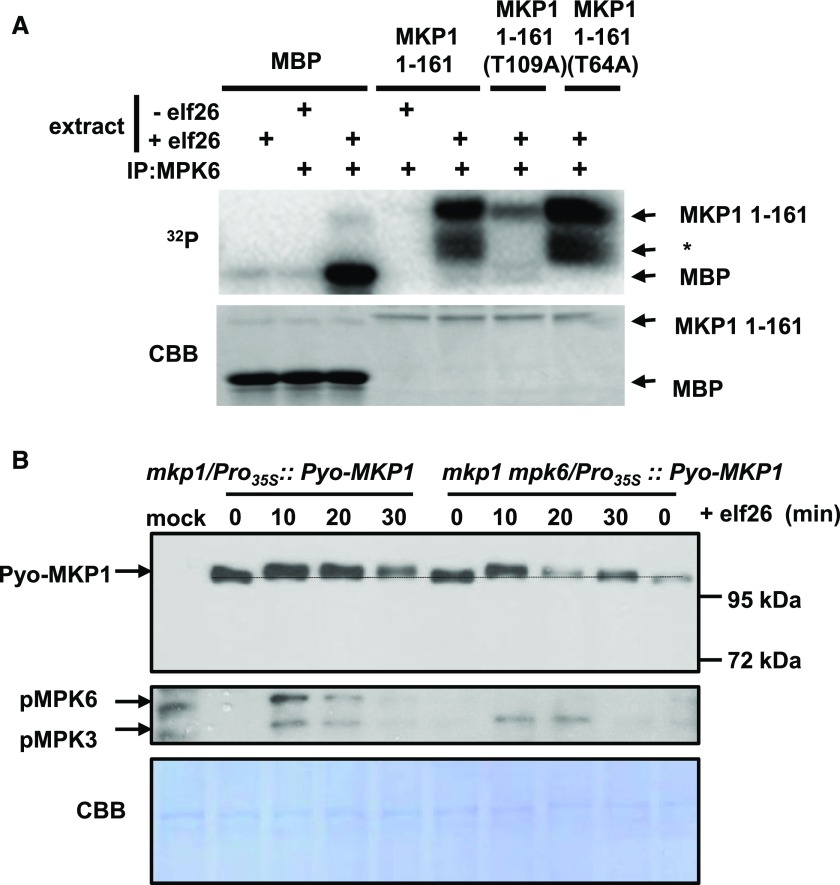
Figure 2.
MKP1 is phosphorylated by elf26-activated MPK6 on Thr-109 in vitro, but loss of MPK6 does not completely prevent elf26-induced phosphorylation in vivo. A, MPK6 was immunoprecipitated from Arabidopsis cells before and after elicitation with 100 nm elf26. The top gel is an autoradiograph of 32P incorporated in MBP, recombinant 6×His-tagged MKP1 1-161, MKP1 1-161 (T109A), or MKP1 1-161 (T64A). The bottom gel is a duplicate gel stained with Coomassie Blue (CBB) to verify equal loading. The asterisk indicates likely partially degraded MKP1. B, Pyo-MKP1 was transiently expressed from the CaMV 35S promoter in Arabidopsis protoplasts isolated from 5-week-old mkp1 (Ws) and mkp1 mpk6 (Ws) adult plants. The protoplasts were treated with 1 µm elf26 for the indicated times. Protein extracts were separated with 8% mini-format (8.3 × 7.3 cm) SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-Glu-Glu antibody to detect the Pyo-MKP1 protein (top) or the anti-phospho-p42/44 MAPKs to detect activated MAPKs (middle). The membrane was stained with Coomassie Blue as a loading control (bottom). Mock control samples were from protoplasts isolated from mkp1 (Ws) without transfection with Pyo-MKP1 plasmid. Experiments were performed at least three times with similar results to those shown.