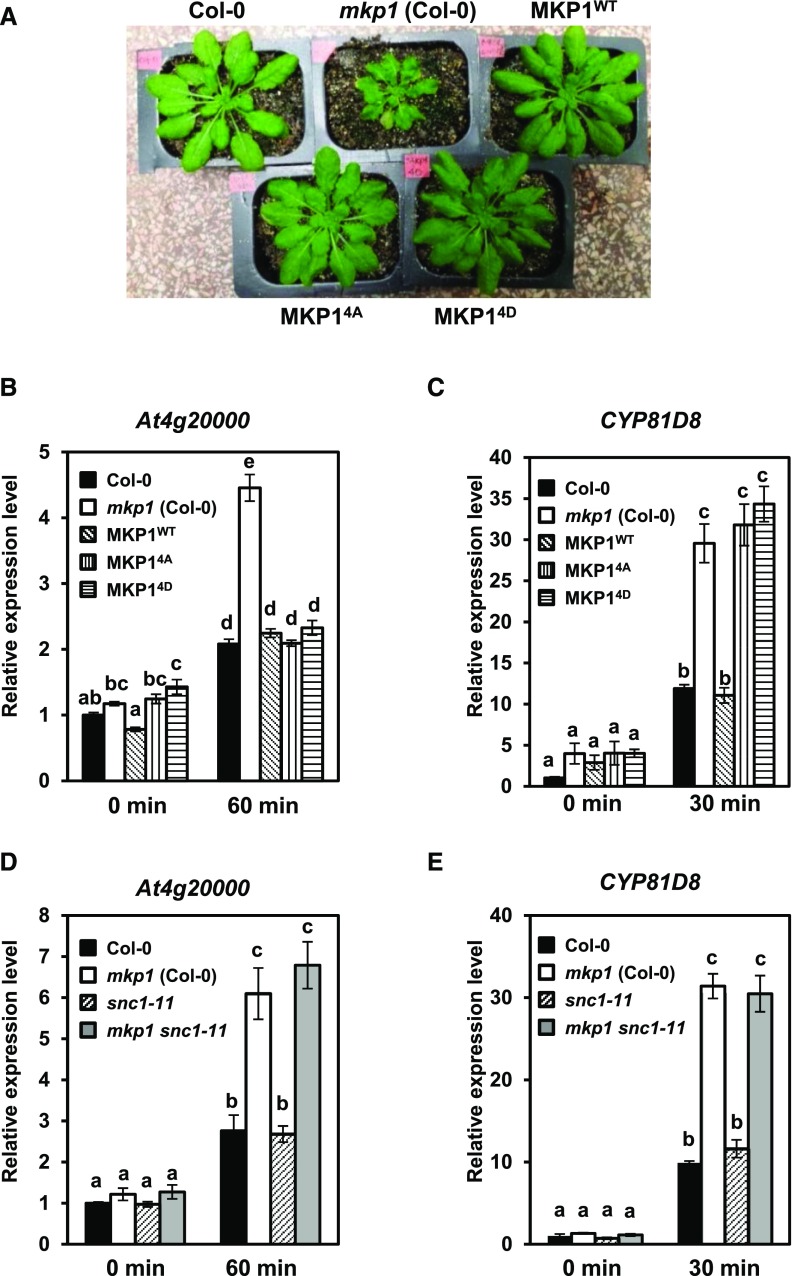
Figure 6.
MKP1 protein lacking phosphorylation sites complements some of the mkp1(Col-0) phenotypes. A, Constitutive defense-related phenotypes of adult mkp1(Col-0) plants compared with wild-type (Col-0) and transgenic mkp1 (Col-0) plants expressing myc-tagged wild-type MKP1 or phosphorylation site mutants MKP14A and MKP14D. The photograph shows 5-week-old adult plants grown on soil. B to E, mRNA levels of PAMP-responsive transcripts of At4g2000 (B and D) or CYP81D8 (C and E) measured by quantitative real-time PCR from 12-d-old seedlings treated with and without 1 μm elf26 for the indicated times. Experiments were performed to test for the requirements of MKP1 phosphorylation (B and C) or for the presence of SNC1 (D and E) in altering the accumulation pattern in mkp1 (Col-0). Transcript levels were normalized to the amount of At2g28390 transcript detected in each sample, then to the transcript level at time 0 in Col-0. Data were pooled from three independent biological experiments with an additional technical replicate for each sample (n = 6). Lowercase letters indicate significant groupings (P < 0.01). The statistical test was performed using ANOVA with Tukey’s pairwise comparison.