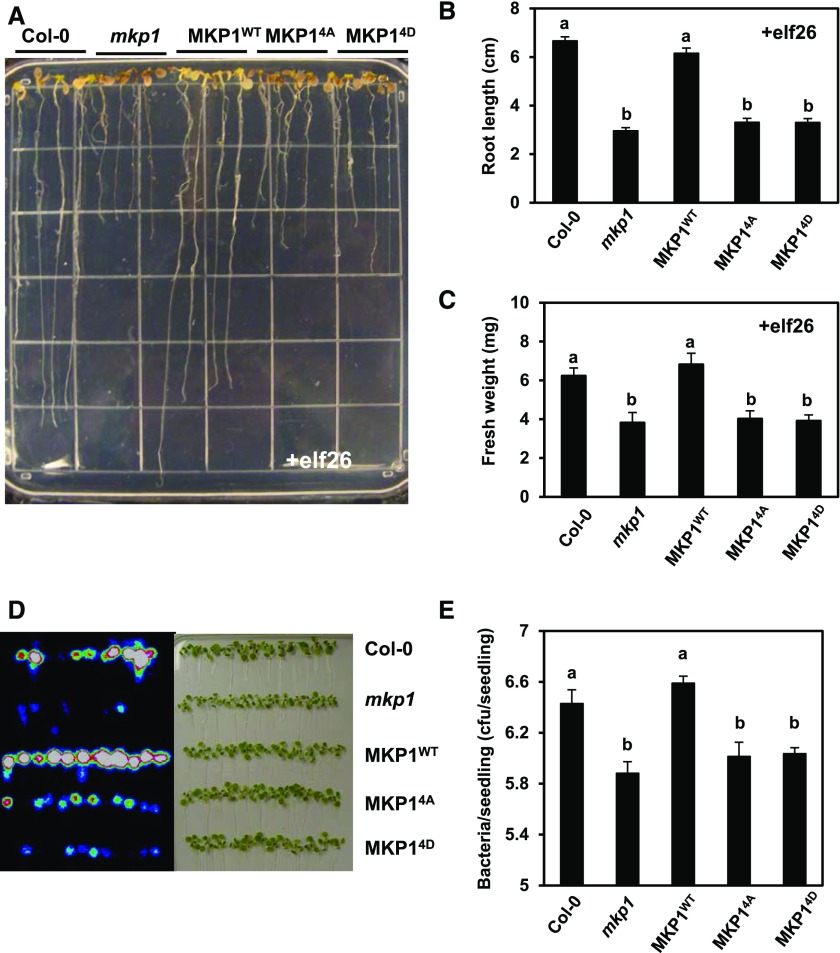
Figure 7.
Phosphorylation of MKP1 is required for regulating elf26-induced growth inhibition and resistance to bacteria. A, Six-old-day seedlings of Col-0, mkp1 (Col-0), MKP1WT, MKP14A, and MKP14D were aseptically transferred from MS agar to the wells of a 24-well microtiter plate containing 1 mL of liquid MS medium with 1 µm elf26 for 14 d. After 14 d, seedlings were placed on an agar surface to photograph the plants, and the image is representative of at least three independent experiments. B and C, Primary root length and fresh weight were measured for the experiment described in A. Graphed are means ± se (n = 24), pooled from three independent experiments. Lowercase letters indicate significant groupings (P < 0.05). The statistical test was performed using ANOVA with Tukey’s pairwise comparison. D, Fourteen-day-old seedlings of Col-0, mkp1 (Col-0), MKP1WT, MKP14A, and MKP14D were immersed in 1 × 107 cfu mL−1 DC3000 LuxCDABE. Three days post infection, seedlings were removed, rinsed with water, and placed on an agar surface. A heat map image of bacterial luminescence in DC3000-infected seedlings detected using a photon-detection camera (left) and a bright-field image of the same seedlings (right) are shown. Results are representative of three independent experiments. E, Bacterial levels in DC3000-infected seedlings 3 d post infection were measured by serial dilution plating of seedling extracts. Graphed are means ± se (n = 6). Lowercase letters indicate significant groupings (P < 0.05). The statistical test was performed using ANOVA with Tukey’s pairwise comparison. Experiments were performed three times with similar results to those shown.